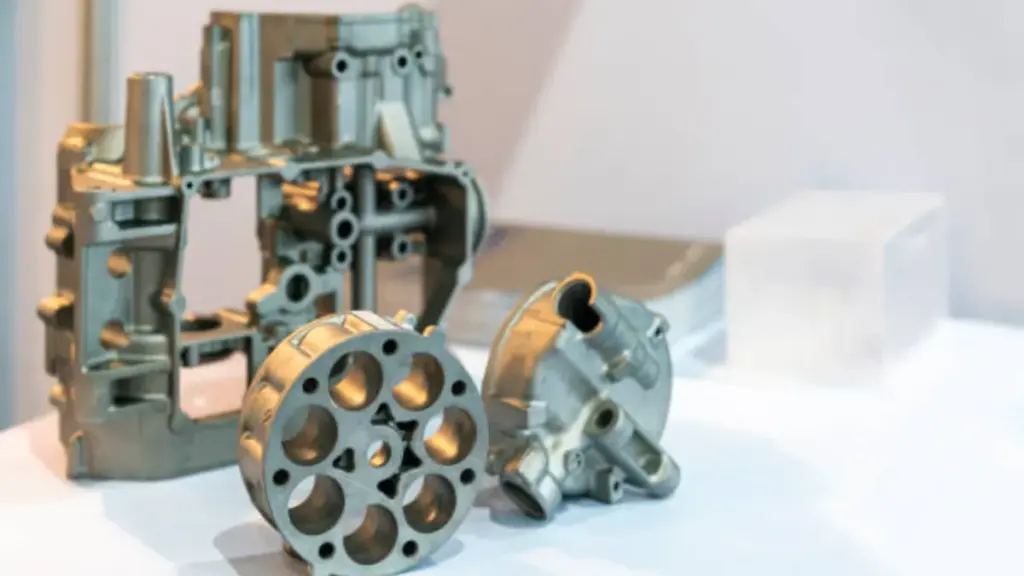
Quando pensi di creare qualcosa da zero, che si tratti di un gadget interessante o di un mobile elegante, potresti imbatterti in due termini: fusione e stampaggio. Entrambi i processi sono essenziali nella produzione, ma hanno le loro vibrazioni e usi unici. COSÌ, qual è la differenza tra fusione e stampaggio? Immergiamoci!
Le basi del casting
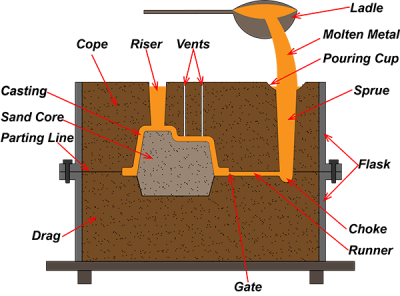
Tipi di processi di fusione
Colata consiste nel versare il materiale liquido in uno stampo e lasciarlo solidificare. È come fare una torta: mescola i tuoi ingredienti (o materiali), versatelo in una padella (lo stampo), e attendere che si stabilizzi. Ecco alcuni metodi di casting popolari:
- Colata in sabbia: Questo è il metodo classico in cui la sabbia viene compattata attorno a un motivo, creando uno stampo. È ottimo per articoli più grandi e relativamente economico.
- Colata di investimento: Mai sentito parlare di fusione a cera persa? Questa tecnica utilizza un modello in cera rivestito in ceramica. Quando la cera si scioglie, ti rimane uno stampo dettagliato, perfetto per disegni complessi!
- Pressofusione: Pensa a questa come alla versione fast food del casting. Il metallo fuso viene iniettato in uno stampo ad alta pressione, rendendolo ideale per la produzione di massa.
- Colata centrifuga: Questo processo fa girare lo stampo, permettendo al materiale di essere forzato contro le pareti dello stampo. È fantastico per realizzare tubi e forme cilindriche.
Vantaggi del casting
La fusione vanta numerosi vantaggi chiave che la rendono un processo di produzione eccezionale:
1. Capacità di creare forme complesse: La fusione eccelle nella produzione di disegni complessi e dettagli raffinati. Se hai bisogno di un pezzo con una geometria complicata, questo metodo può gestirlo con facilità.
2. Versatilità nei materiali: Può ospitare un'ampia gamma di materiali, Compreso:
- Metalli: Alluminio, bronzo, ferro, e altro ancora.
- Plastica: Varie tipologie a seconda della tecnica di fusione.
- Bicchiere: Alcuni metodi possono anche gestire la fusione del vetro.
3. Adattabilità per diverse applicazioni: Che tu abbia bisogno di piccoli oggetti decorativi o di grandi componenti funzionali, la fusione può essere personalizzata per produrre una varietà di dimensioni e forme.
4. Precisione e accuratezza: Il processo di fusione consente un'elevata precisione, garantire che il prodotto finale corrisponda fedelmente al design originale.
5. Efficacia dei costi per grandi cicli di produzione: Mentre la configurazione iniziale può essere più costosa, la fusione diventa conveniente quando si producono grandi quantità dello stesso articolo.
Le basi dello stampaggio
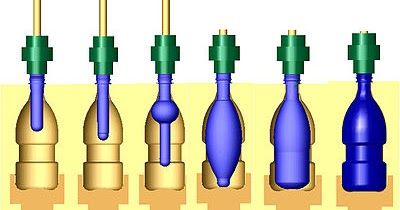
Tipi di processi di stampaggio
Stampaggio, d'altra parte, si tratta di modellare i materiali in forme specifiche. Consideralo come un lavoro manuale con Play-Doh. Puoi strizzarlo e modellarlo come preferisci! Ecco alcuni metodi di stampaggio comuni:
- Stampaggio ad iniezione: Qui è dove la plastica fusa viene iniettata in uno stampo. È molto popolare per realizzare oggetti di uso quotidiano come contenitori e giocattoli.
- Stampaggio per soffiaggio: Questa tecnica viene utilizzata per oggetti cavi come le bottiglie. L'aria viene soffiata in un tubo di plastica riscaldato, che si espande nello stampo.
- Stampaggio rotazionale: Qui, uno stampo viene riempito di polvere e fatto ruotare. Mentre si riscalda, la polvere si scioglie e ricopre l'interno dello stampo, creando prodotti forti e vuoti.
- Termoformatura: Un foglio di plastica viene riscaldato finché non diventa flessibile, poi formato su uno stampo. Questo è comune per i materiali di imballaggio e i vassoi.
Vantaggi dello stampaggio
Lo stampaggio offre numerosi vantaggi significativi, in particolare nell’efficienza produttiva e nella gestione delle risorse:
- Velocità di produzione: Lo stampaggio eccelle nella produzione rapida di grandi quantità di prodotti identici, rendendolo perfetto per la produzione di massa.
- Coerenza: Il processo garantisce che ogni articolo sia uniforme in termini di qualità e aspetto, riducendo la variabilità e migliorando l’affidabilità del prodotto.
- Efficienza dei materiali: Lo stampaggio utilizza in genere meno materiale rispetto alla fusione, che non solo fa risparmiare denaro ma riduce anche gli sprechi.
- Efficacia in termini di costi: Il minor utilizzo di materiale e la produzione rapida si traducono in costi complessivi ridotti, soprattutto quando si producono volumi elevati.
- Benefici ambientali: Riducendo al minimo gli sprechi e utilizzando i materiali in modo più efficiente, lo stampaggio contribuisce a pratiche di produzione più sostenibili.
Differenze chiave tra fusione e stampaggio
Materiali utilizzati
COSÌ, qual è la differenza di fusione e stampaggio nei materiali? La fusione di solito coinvolge metalli o alcune plastiche, mentre lo stampaggio si occupa prevalentemente di materie plastiche. È come scegliere tra biscotti e brownies: ingredienti deliziosi ma diversi!
Panoramica del processo
I processi sono dove risiedono le vere differenze. Nel casting, stai raffreddando un liquido per formare un solido. Con modanatura, spesso riscaldi e rimodelli i materiali. È una danza delle temperature che crea quei meravigliosi prodotti che tutti usiamo.
Applicazioni
Sia la fusione che lo stampaggio sono utilizzati in tutti i settori. Dalle parti automobilistiche agli utensili da cucina, le applicazioni sono vaste. Tuttavia, la fusione è spesso la scelta migliore per le parti pesanti, mentre lo stampaggio è preferito per la leggerezza, articoli prodotti in serie.
Confronto dei costi
Costi di installazione iniziali
La fusione può avere un setup iniziale più elevato a causa della realizzazione degli stampi, soprattutto per disegni complessi. Stampaggio, mentre spesso è più economico predisporre per la produzione di massa, può essere costoso per tirature a basso volume. È come pagare un servizio in abbonamento: più lo usi, più risparmi!
Costi di produzione
In termini di costi di produzione, lo stampaggio generalmente vince per volumi elevati. È efficiente e utilizza meno materiale. Colata, mentre ottimo per pezzi unici, può diventare costoso se produci centinaia dello stesso articolo.
Considerazioni ambientali
Generazione di rifiuti
Entrambi i processi generano rifiuti, ma lo stampaggio in genere produce meno materiale di scarto. Con fusione, potresti avere residui di metallo o sabbia che devono essere smaltiti.
Consumo energetico
Il consumo di energia varia, pure. La fusione può richiedere un elevato consumo di energia a causa del processo di fusione, mentre lo stampaggio può essere più efficiente dal punto di vista energetico una volta impostato. È come paragonare la corsa di una maratona allo sprint; entrambi utilizzano energia, ma ci vuole più resistenza!
Casting contro. Stampaggio: Quale metodo scegliere?
Prima di approfondire le specifiche di ciascun metodo, è essenziale valutare i requisiti del tuo progetto. Poniti le seguenti domande:
1. Di quale materiale hai bisogno?
La fusione è spesso preferita per i metalli e alcune plastiche, mentre lo stampaggio è in genere migliore per una varietà di materie plastiche. Se il tuo progetto prevede componenti metallici, il casting potrebbe essere la strada da percorrere.
2. Quali sono le forme e i dettagli desiderati?
Hai bisogno di disegni intricati o geometrie complesse? Se è così, il casting può offrire la precisione richiesta. La modanatura è eccellente per le forme più semplici, ma potrebbe avere difficoltà con i dettagli fini.
3. Di quante unità hai bisogno?
Stai cercando un piccolo lotto o una produzione di massa? Lo stampaggio eccelle nella produzione di grandi quantità in modo rapido e coerente, rendendolo la scelta ideale per esigenze di volume elevato.
Conclusione
In sintesi, mentre la fusione e lo stampaggio possono sembrare simili, ognuno di essi ha metodi distinti, materiali, e applicazioni. Comprendere la differenza tra stampaggio e fusione può aiutarti a prendere decisioni informate nella produzione o anche quando sei semplicemente curioso di sapere come vengono realizzate le cose. Che tu abbia bisogno di intricati design in metallo o di articoli in plastica prodotti in serie, conoscere il processo giusto può fare la differenza.
Domande frequenti
1. Quali materiali sono comunemente usati nella fusione?
La fusione spesso coinvolge metalli come l'alluminio, ferro, e bronzo, ma è possibile anche colare parte della plastica e del vetro.
2. Quanto tempo richiede in genere il processo di casting?
Il tempo può variare notevolmente a seconda del metodo, ma solitamente richiede più tempo rispetto allo stampaggio a causa dei tempi di raffreddamento.
3. Quali sono i limiti dello stampaggio?
Lo stampaggio può essere meno efficace per progetti complessi ed è generalmente limitato a determinati materiali come la plastica.
4. La fusione e lo stampaggio possono essere utilizzati in modo intercambiabile?
Non proprio. Hanno processi e applicazioni diversi, quindi è importante scegliere in base alle proprie esigenze specifiche.
5. Quali industrie utilizzano principalmente la fusione e lo stampaggio?
Entrambi i processi sono ampiamente utilizzati in settore automobilistico, beni di consumo, aerospaziale, E industrie dell'edilizia, tra gli altri.