다이캐스팅은 현대 제조에서 중추적인 역할을 하는 매혹적인 공정입니다.. 업계의 중추와 같습니다., 자동차 부품부터 전자제품까지 모든 것이 제대로 작동하는지 조용히 확인하세요.. 어떻게 그렇게 많은 복잡한 부품을 그렇게 빨리 만들어낼 수 있는지 궁금하신가요?? 잘, 다이 캐스팅은 비법이다. 이 기술의 기본 사항을 자세히 살펴보고 다이캐스팅의 장점과 단점을 비교해 보겠습니다..
다이캐스팅이란??
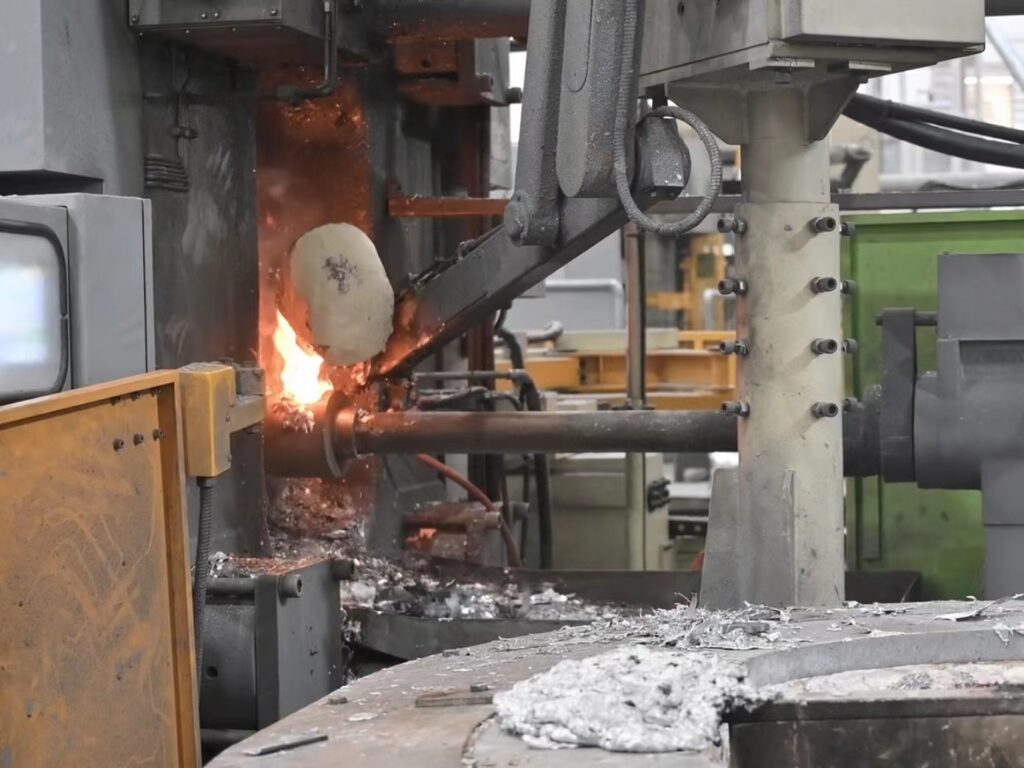

다이 캐스팅은 용융 금속을 고압 하에서 금형 캐비티에 밀어넣는 제조 공정입니다.. 쿠키 커터에 뜨거운 액체 금속을 주입하는 것과 같지만 산업 부품용이라고 생각하세요.. 이 방법은 놀라운 정밀도로 복잡한 형상을 생산하는 것으로 유명합니다..
다이캐스팅의 종류
다이 캐스팅에는 두 가지 주요 맛이 있습니다.: 뜨거운 챔버와 차가운 챔버. 핫 챔버 다이 캐스팅에서, 금속은 금형에 연결된 챔버에서 녹습니다.. 아연과 같이 융점이 낮은 금속에 신속하고 이상적입니다.. 콜드 챔버 다이 캐스팅, 반면에, 금속을 챔버로 옮기기 전에 별도로 녹이는 작업이 포함됩니다.. 이는 융점이 더 높은 알루미늄과 같은 금속을 찾는 데 적합합니다..
다이캐스팅의 장점
다이캐스팅은 괜히 인기만 있는 게 아니다. 다양한 산업 분야에서 사용할 수 있는 다양한 이점을 제공합니다..
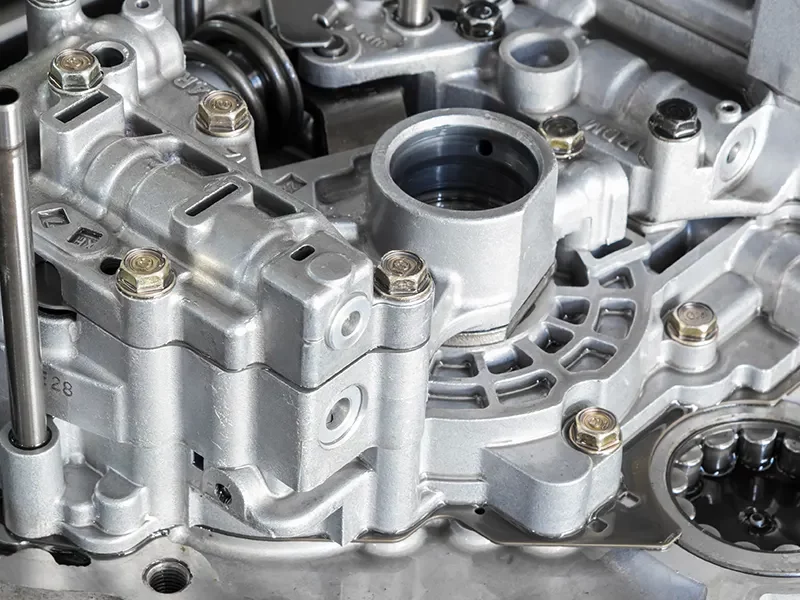
높은 효율성과 생산성
가장 큰 장점 중 하나는 다이캐스팅 얼마나 빠르고 효율적이냐는 거죠. 생산주기가 빠르다, 인상적인 속도로 부품을 꺼내는 중. 을 더한, 올바른 설정으로, 많은 프로세스를 자동화할 수 있습니다, 즉, 엄청난 수작업 없이 일관된 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다..
우수한 품질과 정밀도
다이 캐스팅은 제조의 정밀 예술가와 같습니다.. 다른 방법으로는 복제하기 어려운 엄격한 공차와 복잡한 세부 사항을 얻을 수 있습니다.. 치수 정확도가 최고 수준입니다., 금형에서 바로 매끄러운 표면 마감을 얻을 수 있습니다., 후처리의 필요성 감소.
디자인의 다양성
복잡한 디자인을 염두에 두고? 다이캐스팅으로 처리할 수 있을 것 같습니다. 이 프로세스는 복잡한 형상과 얇은 벽을 가진 부품을 만드는 데 탁월합니다.. 마치 땀 한 방울 흘리지 않고도 상세한 청사진을 현실로 바꿔주는 마술 지팡이를 갖고 있는 것과 같습니다..
재료 절약 및 폐기물 감소
다이캐스팅 세계에서, 낭비하지 마라, 원하지 않는다. 재료를 사용하여 프로세스가 효율적입니다., 최소한의 스크랩 생산. 그리고 생성된 모든 스크랩은 종종 재활용될 수 있습니다., 다른 제조 방법에 비해 더 지속 가능한 옵션이 됩니다..
다이캐스팅의 단점
물론, 어떤 방법도 완벽하지 않다, 다이캐스팅에는 고려해야 할 단점이 있습니다..
높은 초기 비용
다이 캐스팅을 위한 설정은 비용이 많이 들 수 있습니다.. 다이와 장비는 저렴하지 않습니다, 그리고 경제적으로 실행 가능하려면 상당한 수의 부품을 생산해야 합니다.. 이러한 높은 초기 투자는 소규모 운영에 장벽이 될 수 있습니다..
재료 제한
다이캐스팅은 다재다능하지만, 모든 경우에 적용할 수 있는 일률적인 솔루션은 아닙니다.. 사용할 수 있는 금속에 따라 다소 제한이 있습니다.. 일반적으로, 알루미늄과 같은 비철금속에 가장 적합합니다., 아연, 그리고 마그네슘. 강철이나 철로 만든 부품이 필요한 경우, 다른 곳을 찾아봐야 할 거야.
복잡성 및 유지 관리
다이캐스팅의 복잡한 특성으로 인해 도구와 다이는 시간이 지남에 따라 마모될 수 있습니다., 정기적인 유지관리가 필요한. 이러한 유지 관리는 부품의 정밀도와 품질을 유지하는 데 매우 중요합니다., 하지만 이는 전체 비용과 운영 복잡성을 가중시킬 수 있습니다..
크기 제한
다이캐스팅은 중소형 부품에 적합합니다., 하지만 더 큰 구성 요소에는 이상적이지 않습니다.. 생산할 수 있는 부품의 크기와 무게는 다이캐스팅 기계와 금형의 용량에 따라 제한됩니다..
다이캐스팅의 응용
다양한 혜택을 고려하면, 다이캐스팅이 수많은 산업 분야에 진출하는 것은 놀라운 일이 아닙니다..
자동차 산업
다이 캐스팅은 다음과 같은 분야에서 중요한 역할을 합니다. 자동차 부문, 엔진 블록부터 변속기 하우징까지 모든 것을 생산. 내구성을 만드는 능력, 경량 부품으로 연비와 성능 향상에 매우 중요.
가전제품
귀하의 장치가 어떻게 그렇게 세련되고 컴팩트하게 유지되는지 궁금해한 적이 있습니까?? 다이캐스팅이 여기서 핵심 역할을 합니다., 가볍고 강한 부품 제작, 최신 스마트폰에 딱 맞는, 노트북, 그리고 기타 전자 기기.
항공우주 및 국방
정밀도와 신뢰성이 가장 중요한 산업 분야, 다이 캐스팅이 빛난다. 극한의 조건을 견딜 수 있는 부품을 제조하는 데 사용됩니다., 항공우주 및 방위 분야에 이상적입니다..
가전제품
주방용품부터 전동공구까지, 다이캐스팅이 무대 뒤에서, 이러한 제품의 견고성과 신뢰성 보장. 복잡한 형상의 부품을 생산할 수 있다는 것은 설계자가 제조상의 한계에 얽매이지 않고 자유롭게 혁신할 수 있음을 의미합니다..
다이 캐스팅 대. 기타 캐스팅 방법
캐스팅 방법을 결정할 때, 다이캐스팅과 기타 일반적인 기술의 차이점을 이해하는 것이 중요합니다.. 각 방법에는 고유한 장점과 단점이 있습니다., 다양한 응용 분야에 적합하게 만들기.
다이 캐스팅 대. 모래 주조
모래 주조, 가장 오래된 주조 기술 중 하나, 모래를 주형으로 만들어 다이캐스팅과 비교하면 다음과 같습니다.:
- 다이캐스팅은 탁월한 치수 정확성과 보다 매끄러운 표면 마감을 제공합니다., 모래 주조에는 종종 추가 가공이 필요합니다..
- 고압사출로 다이캐스팅이 더 빠릅니다., 느린 모래 금형 공정과 달리.
- 샌드 캐스팅은 다양한 금속을 처리합니다., 철합금을 포함한, 다이캐스팅은 알루미늄과 같은 비철금속으로 제한됩니다., 아연, 그리고 마그네슘.
- 다이캐스팅은 초기 설정 비용이 더 높지만, 대규모 생산에 더욱 비용 효율적이 됩니다., 모래 주조는 초기 투자가 적기 때문에 소규모 배치 또는 대규모 구성 요소에 더 적합합니다..
다이 캐스팅 대. 투자 주조
투자 주조, 또는 분실된 왁스 주조, 세라믹으로 코팅된 왁스 모형으로 주형을 만듭니다.. 다이캐스팅에 비해:
- 인베스트먼트 주조를 통해 더욱 미세한 디테일과 복잡한 디자인을 얻을 수 있습니다., 복잡한 형상에 이상적입니다..
- 다이캐스팅은 일반적으로 더 매끄러운 표면 마감을 제공합니다., 매몰 주조에는 추가 마무리가 필요한 경우가 많습니다..
- 다이캐스팅은 빠른 사이클 시간으로 대량 생산에 더 효율적입니다., 매몰 주조는 중소 규모의 경우 더 느리고 더 좋습니다..
- 인베스트먼트 주조는 더 넓은 범위의 금속으로 더욱 다양해졌습니다., 스테인리스강과 같은 고융점 합금 포함, 다이캐스팅은 비철금속으로 제한되어 있지만.
다이 캐스팅 제조업체를 선택하는 방법
선택 올바른 다이캐스팅 제조r은 생산 품질과 효율성을 보장하는 데 매우 중요합니다.. 결정을 내리는 데 도움이 되는 몇 가지 주요 요소와 질문은 다음과 같습니다..
- 경험과 전문성: 다이캐스팅 분야에서 입증된 실적을 보유한 제조업체를 찾으세요., 특히 귀하와 유사한 부품을 생산한 경험이 있는 분. 그들의 전문 지식은 최종 제품의 품질과 신뢰성에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다..
- 역량과 기술: 제조업체의 생산 능력을 평가하세요., 주조할 수 있는 금속 유형을 포함하여, 처리할 수 있는 부품의 크기와 복잡성, 그리고 그들이 사용하는 기술. 현대의, 잘 관리된 장비와 첨단 기술로 효율성과 품질을 향상시킬 수 있습니다..
- 품질 보증: 제조업체가 강력한 품질 관리 프로세스를 갖추고 있는지 확인하십시오.. ISO 등의 인증 9001 높은 기준을 유지하려는 의지를 나타낼 수 있습니다.. 검사 방법과 결함 및 불일치 처리 방법에 대해 문의하십시오..
- 리드타임과 유연성: 제조업체의 리드 타임과 생산 일정 변경을 수용할 수 있는 능력을 고려하십시오.. 신뢰할 수 있는 제조업체는 품질 저하 없이 마감일을 준수하고 요구 사항에 적응할 수 있어야 합니다..
- 비용과 가치: 비용이 중요한 요소이기는 하지만, 제공되는 가치와 균형을 맞추는 것이 중요합니다. 전체 패키지 평가, 품질을 포함한, 서비스, 그리고 지원, 단지 개당 가격이 아니라.
결론
다이 캐스팅은 제조 분야의 강자입니다., 효율성의 독특한 조합을 제공합니다., 정도, 그리고 다양성. 몇 가지 어려움이 따르지만, 장점이 단점보다 더 큰 경우가 많습니다., 특히 대량 생산 시나리오에서. 기술이 발전함에 따라, 다이캐스팅의 미래는 그 어느 때보다 밝아 보입니다, 더 많은 혁신과 개선을 약속합니다.
다이 캐스팅에 관한 FAQ
1. 다이캐스팅 금형의 수명은 얼마나 됩니까??
다이캐스팅 금형의 수명은 주조되는 금속 유형 및 금형의 복잡성과 같은 요인에 따라 크게 달라질 수 있습니다.. 일반적으로, 금형은 수만에서 수십만 주기까지 지속될 수 있습니다..
2. 소규모 생산에 다이캐스팅을 사용할 수 있습니까??
다이캐스팅은 일반적으로 초기 비용이 높기 때문에 대규모 생산에 더 비용 효율적입니다., 부품이 특히 복잡하거나 다른 정당화 요인이 있는 경우 소규모 작업에 사용할 수 있습니다..
3. 다이캐스팅은 다른 주조 방법과 어떻게 비교됩니까??
다이 캐스팅으로 뛰어난 정밀도 제공, 더 빠른 생산 시간, 다른 주조 방법에 비해 표면 마감이 우수합니다.. 하지만, 또한 더 높은 초기 투자가 필요하고 사용할 수 있는 금속 측면에서 유연성이 떨어집니다..
4. 다이캐스팅의 일반적인 결함은 무엇입니까??
일반적인 결함에는 다공성이 포함됩니다., 이는 주조 부품의 작은 공극입니다., 금속이 금형을 완전히 채우지 못하는 잘못된 실행, 그리고 표면 흠집. 적절한 프로세스 제어 및 유지 관리를 통해 이러한 문제를 최소화할 수 있습니다..
5. 다이캐스팅에 적합한 금속을 선택하는 방법?
금속 선택은 응용 분야의 요구 사항에 따라 달라집니다.. 알루미늄은 가볍고 강하다, 아연은 높은 정밀도와 주조 용이성을 제공합니다., 마그네슘은 가볍고 기계 가공이 쉽습니다.. 각 금속은 다양한 용도에 적합한 고유한 특성을 가지고 있습니다..


















