Die CNC-Bearbeitung ist ein modernster Herstellungsprozess, bei dem computergesteuerte Bedienelemente zum Betrieb und zur Manipulation von Werkzeugmaschinen verwendet werden. Diese Technologie hat die Art und Weise revolutioniert, wie Produkte entworfen und produziert werden, Erhöhte Präzision zulassen, Effizienz, und Anpassung. In diesem Leitfaden, Wir werden die Grundlagen der CNC -Bearbeitung untersuchen, einschließlich seiner Vorteile, Arten von Maschinen, Komponenten, Prozesse, Materialien und mehr .
Was ist CNC -Bearbeitung?
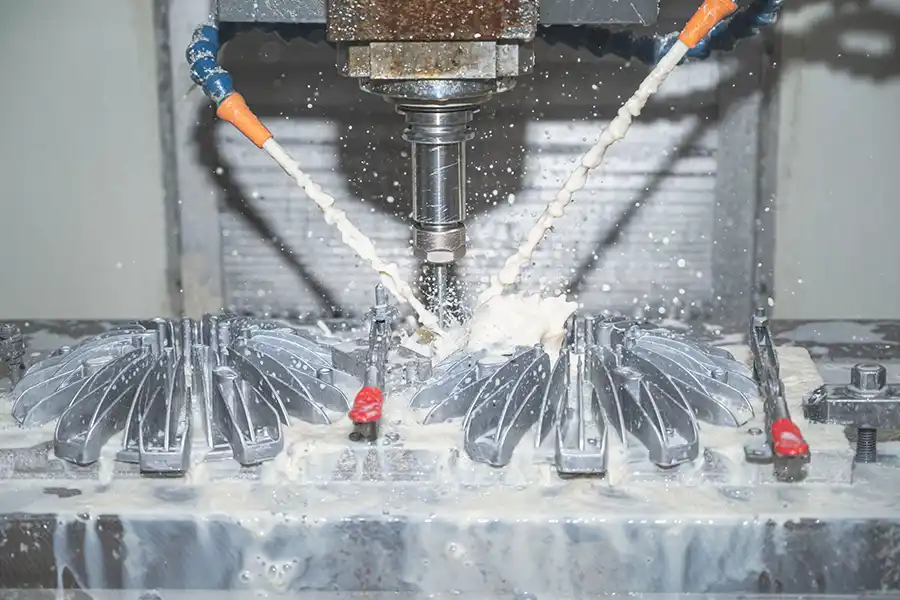

CNC-Bearbeitung, was steht für Computer numerische Steuerbearbeitung, ist ein Herstellungsprozess, bei dem computergesteuerte Steuerelemente zum Betrieb und Manipulieren von Werkzeugmaschinen verwendet werden. Diese Technologie ermöglicht die automatisiert und präzise Gestaltung verschiedener Materialien, um komplexe Komponenten und Teile zu erstellen.
Vorteile der CNC -Bearbeitung

CNC-Bearbeitung bietet eine breite Palette von Vorteilen, Machen Sie es zu einer vielseitigen und unverzichtbaren Technologie in modernen Herstellungsprozessen.
Präzision und Genauigkeit
Einer der wichtigsten Vorteile der CNC -Bearbeitung ist die Fähigkeit, hoch genaue und präzise Teile zu produzieren. Mit computergesteuerter Automatisierung, CNC -Maschinen können enge Toleranzen und Konsistenz erzielen, die mit manuellen Prozessen schwer zu replizieren sind.
Effizienz und Produktivität
Die CNC -Bearbeitung bietet eine erhöhte Effizienz und Produktivität im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Fertigungsmethoden. Die Automatisierung von Prozessen verkürzt die Zeit und die Arbeit, die zur Herstellung von Teilen erforderlich sind, Dies führt zu schnelleren Umlaufzeiten und höherer Ausgabe.
Kosteneffizienz
Während die anfängliche Investition in CNC -Bearbeitungsgeräte erheblich sein kann, Die langfristigen Kosteneinsparungen sind erheblich. Die Automatisierung und Effizienz der CNC -Bearbeitung kann zu reduzierten Arbeitskosten führen, minimierte Materialabfälle, und Gesamtkosteneinsparungen in der Produktion.
Komplexe Designs
Die CNC -Bearbeitung ermöglicht die Erstellung komplizierter und komplexer Designs, die mit herkömmlichen Bearbeitungsmethoden schwierig oder unmöglich zu erreichen sind. Die Fähigkeit, komplizierte Werkzeugwege und Geometrien zu programmieren.
Arten von CNC -Maschinen

CNC -Fräsmaschinen
CNC -Fräsmaschinen verwenden Rotationsschneider, um Material aus einem Werkstück zu entfernen. Sie sind vielseitige Maschinen, die eine Vielzahl von Formen und Größen schaffen können.
CNC -Drehmaschinen
CNC -Drehmaschinen werden verwendet, um zylindrische Teile durch Drehen des Werkstücks zu erstellen, während ein Schneidwerkzeug Material entfernt. Diese Maschinen eignen sich ideal, um Teile mit Rotationssymmetrie zu produzieren.
CNC -Plasmaschneider
CNC-Plasmaschneider verwenden einen Hochgeschwindigkeitsstrom ionisierter Gas, um Materialien wie Metall zu durchschneiden. Sie werden üblicherweise für Metallherstellung und Schneidanwendungen verwendet.
CNC -Laserschneider
CNC-Laserschneider verwenden einen leistungsstarken Laser, um Materialien mit Präzision und Geschwindigkeit zu durchschneiden. Sie sind ideal für komplizierte Schnitt- und Gravuranwendungen.
Grundkomponenten von CNC -Maschinen
Regler
Der Controller dient als Gehirn der CNC -Maschine, Interpretation der Entwurfsdaten und Umwandlung in Bewegungsbefehle für die Werkzeugmaschinen.
Werkzeugmaschine
Die Werkzeugmaschine ist die physische Ausrüstung, mit der das Werkstück gestaltet und geschnitten wird. Es wird vom CNC -System gesteuert, um die erforderlichen Vorgänge auszuführen.
Werkstück
Das Werkstück ist der Rohstoff, der während des Bearbeitungsprozesses geformt und modifiziert wird. Es ist für die Verarbeitung an der Werkzeugmaschine befestigt.
Schneidwerkzeug
Das Schneidwerkzeug ist das Werkzeug, das Material aus dem Werkstück entfernt, um die gewünschte Form zu erstellen. Es wird vom Werkzeugmaschine gesteuert, um präzise Schneidvorgänge durchzuführen.
Schritt für Schritt CNC -Bearbeitungsvorgang

Ein tieferes Verständnis der Grundlagen von CNC -Bearbeitung zu erlangen, Es ist wichtig, seinen Betriebsmechanismus zu verstehen. Erkunden wir die folgenden fünf Schritte.
#1: Entwerfen des Teils
Der erste Schritt im CNC -Bearbeitungsprozess besteht darin, das Teil mit CAD -Software zu entwerfen. Der Designer erstellt ein digitales Modell des Teils, einschließlich Abmessungen, Merkmale, und Toleranzen.
#2: Programmieren der Maschine
Sobald das Teil entworfen wurde, Die CAM -Software generiert ToolPaths und Anweisungen für die CNC -Maschine. Diese Anweisungen geben die Bewegungen der Werkzeugmaschinen und die zu durchgeführten Schneidvorgänge an.
#3: Einrichten der Maschine
Die CNC -Maschine wird gemäß den von der CAM -Software generierten Anweisungen eingerichtet. Dies beinhaltet das Laden des Werkstücks, Sichern Sie es an der Werkzeugmaschine, und kalibrieren Sie die Maschine für den spezifischen Betrieb.
#4: Ausführung des Vorgangs
Mit der Maschine eingerichtet und programmiert, Der CNC -Bearbeitungsvorgang kann beginnen. Die Maschine folgt den vordefinierten Werkzeugpfängen und führt die Schneidvorgänge aus, um das Werkstück wie im Design angegeben zu formen.
#5: Qualitätskontrolle
Während des gesamten Bearbeitungsprozesses, Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen werden durchgeführt, um sicherzustellen, dass der fertige Teil den erforderlichen Spezifikationen entspricht. Es werden Inspektionen und Messungen durchgeführt, um die Genauigkeit und Qualität des Endprodukts zu überprüfen.
Materialien, die in der CNC -Bearbeitung verwendet werden
Es gibt eine breite Palette von Materialien, die in CNC -Bearbeitungsverfahren üblicherweise verwendet werden.
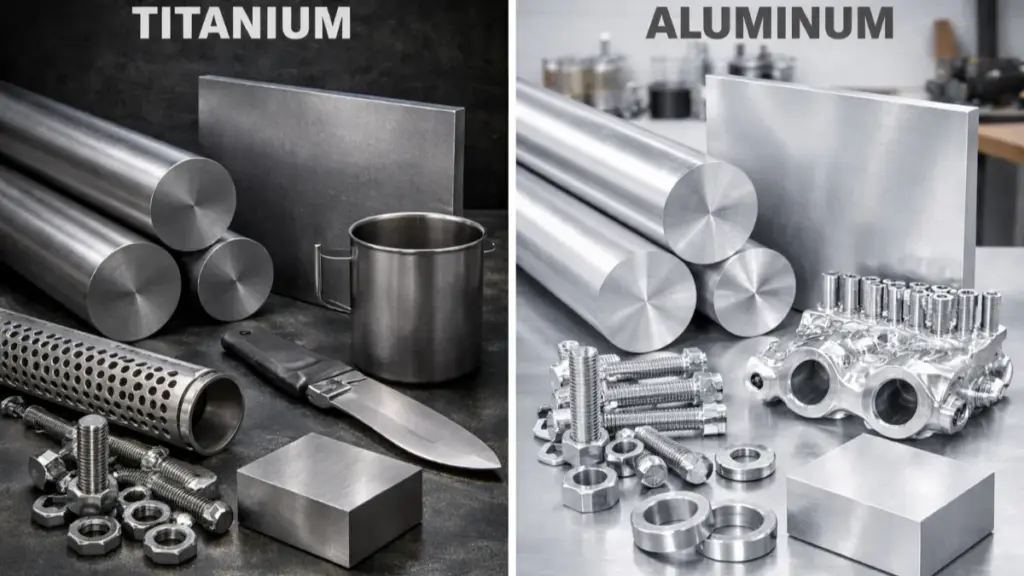
Metalle
Metalle wie Aluminium, Stahl, und Titan werden häufig in der CNC -Bearbeitung aufgrund ihrer Stärke verwendet, Haltbarkeit, und Bearbeitbarkeit. Diese Materialien sind ideal für eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen in verschiedenen Branchen.
Kunststoffe
Kunststoffe wie ABS, PVC, und Acrylics sind aufgrund ihrer Vielseitigkeit beliebte Wahl für die CNC -Bearbeitung, Leichte Eigenschaften, und Wirtschaftlichkeit. Sie werden in Anwendungen verwendet, bei denen Gewicht, Korrosionsbeständigkeit, und Ästhetik sind wichtig.
Holz
Holzmaterial wie Hartholz, Weichholz, und Sperrholz werden auch in der CNC -Bearbeitung für Anwendungen wie Möbel verwendet, Schränke, und Dekorationsartikel. Holz bietet eine natürliche Ästhetik und eine einfache Verwirrbarkeit.
Verbundwerkstoffe
Verbundwerkstoffe, die aus zwei oder mehr Materialien mit unterschiedlichen Eigenschaften bestehen, in der CNC -Bearbeitung an Popularität erlangen. Kohlefaser, Glasfaser, und Kevlar-Verbundwerkstoffe bieten hohe Verhältnisse zu Gewicht und werden in der Luft- und Raumfahrt verwendet, Automobil, und Sportgüterindustrien.
Anwendungen der CNC -Bearbeitung
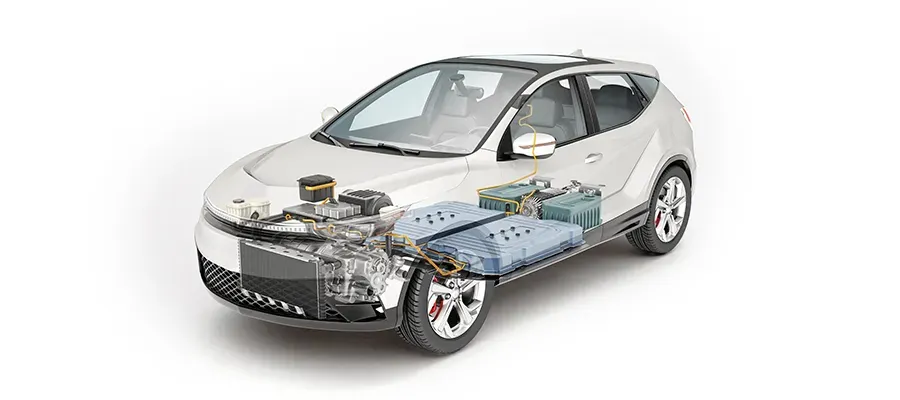

Wegen seiner Vielseitigkeit und zahlreichen Vorteilen, CNC -Bearbeitung findet umfangreiche Anwendungen in verschiedenen Industriesektoren.
Luft-und Raumfahrtindustrie
Die Luft- und Raumfahrtindustrie stützt sich stark auf die CNC -Bearbeitung für die Herstellung von Flugzeugkomponenten, Motorteile, und strukturelle Elemente. Die Präzision, Genauigkeit, und Wiederholbarkeit der CNC -Bearbeitung macht es in der Herstellung von Luft- und Raumfahrt unverzichtbar.
Automobilindustrie
Im Automobilindustrie, Die CNC -Bearbeitung wird verwendet, um eine Vielzahl von Komponenten zu erzeugen, von Motorteilen bis zu Körperpaneele. Die Effizienz und Konsistenz der CNC -Bearbeitung sorgen dafür, dass Automobilhersteller die anspruchsvollen Qualitätsstandards der Branche erfüllen können.
Medizinische Industrie
Die CNC -Bearbeitung spielt eine entscheidende Rolle in der medizinischen Industrie für die Herstellung von chirurgischen Instrumenten, Implantate, und medizinische Geräte. Die Fähigkeit, komplexe und maßgeschneiderte Teile mit engen Toleranzen zu erstellen.
Elektronikindustrie
Der Elektronikindustrie stützt sich auf CNC -Bearbeitung für die Produktion von Leiterplatten, Gehege, und andere elektronische Komponenten. Die genauen und komplizierten Schneidfähigkeiten von CNC-Maschinen ermöglichen es den Elektronikherstellern, hochwertige Produkte mit Präzision und Genauigkeit zu schaffen.
Fortschritte in der CNC -Technologie
In diesem Abschnitt, Wir werden uns mit den neuesten Innovationen und technologischen Fortschritten befassen, die die Entwicklung der CNC -Bearbeitung vorantreiben. Entdecken Sie, wie diese Fortschritte die Landschaft der Präzisionsherstellung und revolutionalisierten industriellen Prozesse in verschiedenen Sektoren umformieren.
Automatisierung
Fortschritte bei Automatisierungstechnologien haben die CNC -Bearbeitung revolutioniert, Ermöglichen Sie eine erhöhte Produktivität, Reduzierte Arbeitskosten, und verbesserte Prozesseffizienz. Automatisiertes Werkzeugwechsel, Roboterbelastung, und integrierte Qualitätskontrollsysteme sind nur einige der Automatisierungsfunktionen, die den CNC -Bearbeitungsvorgang verbessern.
Künstliche Intelligenz
Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) wird in CNC -Bearbeitungssysteme integriert, um Schnittparameter zu optimieren, Vorhersage der Werkzeugkleidung, und die Prozesskontrolle verbessern. AI-Algorithmen analysieren Daten in Echtzeit, um Anpassungen und Optimierungen vorzunehmen, die die Bearbeitungsleistung und -qualität verbessern.
3D Druckintegration
Die Integration von 3D -Drucktechnologien mit CNC -Bearbeitung verändert die Produktionslandschaft. Hybridmaschinen, die additive und subtraktive Fertigungsfunktionen kombinieren, bieten neue Möglichkeiten zur Schaffung komplexer Geometrien, Verringerung von Materialabfällen, und zunehmende Designflexibilität.
Industrie 4.0
Das Konzept der Industrie 4.0, Dies konzentriert sich auf die digitale Transformation von Herstellungsprozessen, treibt Innovation in der CNC -Bearbeitung vor. Intelligente Fabriken, miteinander verbundene Maschinen, und datengesteuerte Entscheidungsfindung ermöglichen es den Herstellern, die Produktion zu optimieren, Effizienz erhöhen, und passen Sie sich an sich verändernde Marktanforderungen an.
Abschluss
Abschließend, Die CNC -Bearbeitung ist eine leistungsstarke und vielseitige Fertigungstechnologie, die eine breite Palette von Vorteilen bietet, Anwendungen, und Möglichkeiten für Wachstum und Innovation. Erlernen der Grundlagen der CNC -Bearbeitung, Die Arten von Maschinen und Komponenten sind für Hersteller von entscheidender Bedeutung, die diese Technologie in ihrem Betrieb nutzen möchten. Mit seiner Fähigkeit, komplexe Designs zu produzieren, Arbeiten Sie mit einer Vielzahl von Materialien, und sorgen für verschiedene Branchen, Die CNC -Bearbeitung ist weiterhin ein wesentliches Werkzeug für moderne Herstellungsprozesse.
FAQs bei CNC -Bearbeitung
1. Was ist CNC -Fräste?
Das CNC-Mühlen ist ein Herstellungsprozess, bei dem computergesteuerte Rotations-Schneidwerkzeuge verwendet werden, um Material aus einem Werkstück zu entfernen.
2. Was dreht sich CNC?
CNC Drehung ist ein Herstellungsprozess, bei dem ein Schneidwerkzeug verwendet wird, um Material aus einem rotierenden Werkstück zu entfernen, um zylindrische Teile zu erstellen.
3. Was ist ein CNC -Router??
Ein CNC-Router ist eine computergesteuerte Schneidemaschine, die zum Schneiden verschiedener Materialien wie Holz verwendet wird, Kunststoff, und Metalle.
4. Wofür steht CNC bei der Bearbeitung??
In Bearbeitung, CNC steht für Computer Numerical Control, Dies bezieht sich auf die Automatisierung von Werkzeugmaschinen über Computerprogramme, um präzise und komplexe Bearbeitungsvorgänge auszuführen.


















