A resistência ao escoamento é uma propriedade fundamental na engenharia, especialmente quando se trata da versatilidade das ligas de alumínio. Estas ligas desempenham um papel crucial em diversas indústrias devido às suas propriedades excepcionais. Vamos nos aprofundar na importância do limite de escoamento e explorar a importância das ligas de alumínio na engenharia.
O que é resistência ao rendimento?
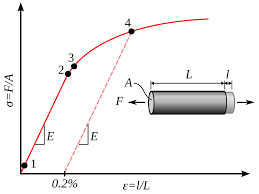
O limite de escoamento é a medida da tensão máxima que um material pode suportar sem sofrer deformação permanente.. É um parâmetro crítico para determinar a integridade estrutural e o desempenho dos materiais. O limite de escoamento das ligas de alumínio é avaliado através de testes padronizados, fornecendo insights essenciais sobre seu comportamento mecânico sob diferentes condições.
Ligas de alumínio e suas aplicações

Ligas de alumínio são apreciados por sua natureza leve, resistência à corrosão, e impressionante relação resistência-peso. Eles encontram amplas aplicações em diversos setores, incluindo aeroespacial, automotivo, construção, e eletrônicos de consumo. De componentes de aeronaves a utensílios domésticos de uso diário, ligas de alumínio são indispensáveis na engenharia moderna.
6061 Resistência ao rendimento do alumínio
Propriedades de 6061 Alumínio
6061 alumínio é conhecido por suas excelentes propriedades mecânicas, incluindo um limite de escoamento de aproximadamente 276 MPa (40,000 psi). Possui soldabilidade notável, resistência à corrosão, e usinabilidade, tornando-o uma escolha popular para diversas aplicações.
Aplicações e vantagens de 6061 Alumínio
Esta liga versátil é amplamente utilizada em componentes estruturais, quadros, e aplicações marítimas. Sua força excepcional, juntamente com sua natureza leve, torna-o ideal para peças que exigem alta resistência e durabilidade.
7075 Resistência ao rendimento do alumínio
Propriedades de 7075 Alumínio
7075 o alumínio é uma liga de alta resistência com um impressionante limite de escoamento de aproximadamente 503 MPa (73,000 psi). Embora ofereça propriedades mecânicas excepcionais, é menos resistente à corrosão em comparação com 6061 alumínio.
Aplicações e vantagens de 7075 Alumínio
Utilizado principalmente em aplicações aeroespaciais e militares, 7075 o alumínio é preferido por sua excelente relação resistência-peso. É comumente empregado em componentes de aeronaves, peças de mísseis, e elementos estruturais de alta tensão onde a resistência é fundamental.
2024 Resistência ao rendimento do alumínio
Propriedades de 2024 Alumínio
2024 o alumínio é reconhecido por sua excelente resistência e rigidez, ostentando uma força de rendimento de cerca 324 MPa (47,000 psi). Apresenta boa usinabilidade e resistência à fadiga, tornando-o adequado para diversas aplicações de engenharia.
Aplicações e vantagens de 2024 Alumínio
Amplamente utilizado na indústria aeroespacial, automotivo, e aplicações estruturais, 2024 o alumínio é preferido por sua alta resistência e resistência à fadiga. Encontra aplicações em estruturas de aeronaves, longarinas de asa, e equipamentos esportivos de alto desempenho.
6063 Resistência ao rendimento do alumínio
Propriedades de 6063 Alumínio
6063 o alumínio oferece uma resistência ao escoamento de aproximadamente 241 MPa (35,000 psi) juntamente com excelente resistência à corrosão e conformabilidade. É conhecido por seu acabamento superficial liso e é frequentemente usado em aplicações arquitetônicas e decorativas..
Aplicações e vantagens de 6063 Alumínio
Esta liga é comumente empregada em formas extrudadas para fins arquitetônicos, janela de quadros, molduras de portas, e vários componentes estruturais. Sua combinação de força, conformabilidade, e a resistência à corrosão o tornam uma escolha versátil em construção e design.
5052 Resistência ao rendimento do alumínio
Propriedades de 5052 Alumínio
5052 o alumínio possui uma resistência ao escoamento de cerca de 193 MPa (28,000 psi) e é altamente considerado por sua excelente resistência à corrosão e soldabilidade. É uma liga não tratável termicamente, conhecida por sua conformabilidade e durabilidade.
Aplicações e vantagens de 5052 Alumínio
Amplamente utilizado em marinha, automotivo, e aplicativos eletrônicos, 5052 o alumínio é preferido por sua excepcional resistência à corrosão por água salgada. É comumente usado em componentes marinhos, painéis de veículos, e gabinetes eletrônicos onde a resistência à corrosão é crucial.
Análise Comparativa da Resistência ao Escoamento
Comparando 6061, 7075, 2024, 6063, e 5052
Cada liga de alumínio oferece propriedades e vantagens únicas. Enquanto 7075 o alumínio possui a maior resistência ao escoamento, 6061 o alumínio é valorizado por sua excelente combinação de resistência, soldabilidade, e resistência à corrosão. 2024 o alumínio é conhecido por sua alta resistência e resistência à fadiga, tornando-o adequado para aplicações aeroespaciais. Por outro lado, 6063 e 5052 alumínio são preferidos por sua excepcional conformabilidade, resistência à corrosão, e versatilidade em aplicações arquitetônicas e marítimas.
Fatores que afetam o limite de escoamento em ligas de alumínio
Vários fatores influenciam o limite de escoamento das ligas de alumínio, incluindo composição da liga, processos de tratamento térmico, e trabalho de endurecimento. A composição da liga desempenha um papel significativo na determinação das propriedades mecânicas das ligas de alumínio, enquanto processos de tratamento térmico, como têmpera e envelhecimento, podem aumentar sua resistência e durabilidade. Endurecimento por trabalho, resultante de deformação plástica, aumenta ainda mais a resistência ao escoamento das ligas de alumínio.
Teste de resistência ao escoamento de ligas de alumínio
Métodos de teste padrão
A resistência ao escoamento das ligas de alumínio é normalmente determinada através de testes padronizados, como testes de tensão ou testes de compressão.. Esses testes envolvem a aplicação de cargas controladas ao material até que ele sofra deformação plástica., permitindo que os engenheiros avaliem com precisão seu limite de escoamento.
Testes de laboratório vs.. Teste de campo
Embora os testes de laboratório forneçam medições precisas sob condições controladas, testes de campo oferecem insights reais sobre o desempenho de ligas de alumínio em aplicações reais. Ambos os métodos são valiosos na avaliação do limite de escoamento e das propriedades mecânicas das ligas de alumínio., garantindo sua adequação para requisitos específicos de engenharia.
Conclusão
Para concluir, a resistência ao escoamento é um parâmetro crítico na avaliação de ligas de alumínio, determinar sua integridade estrutural e desempenho em diversas aplicações de engenharia. Da alta resistência 7075 alumínio ao versátil 6061 liga, cada liga de alumínio oferece propriedades e vantagens únicas. À medida que os avanços continuam na composição da liga, tecnologias de tratamento térmico, e métodos de teste, o futuro das ligas de alumínio na engenharia parece promissor, oferecendo soluções inovadoras para uma ampla gama de aplicações.
Perguntas frequentes
1. Qual é a diferença entre resistência ao escoamento e resistência à tração?
O limite de escoamento é a tensão máxima que um material pode suportar sem sofrer deformação permanente., enquanto a resistência à tração é a tensão máxima que pode suportar antes de fraturar sob tensão. O limite de escoamento indica o ponto em que um material começa a se deformar plasticamente, enquanto a resistência à tração representa sua resistência máxima sob tensão.
2. Como o tratamento térmico afeta o limite de escoamento?
Processos de tratamento térmico, como têmpera e envelhecimento, podem afetar significativamente o limite de escoamento das ligas de alumínio. A têmpera envolve o resfriamento rápido do material para aumentar sua resistência, enquanto o envelhecimento ou o endurecimento por precipitação melhoram ainda mais suas propriedades mecânicas, incluindo limite de escoamento.
3. As ligas de alumínio podem ser usadas em aplicações de alto estresse??
Sim, certas ligas de alumínio, como 7075 e 2024 são projetados especificamente para aplicações de alto estresse, incluindo aeroespacial, militares, e engenharia estrutural. Essas ligas oferecem relações resistência-peso excepcionais, tornando-os adequados para aplicações exigentes onde a resistência e a durabilidade são fundamentais.
4. Quais são os benefícios ambientais do uso de ligas de alumínio?
As ligas de alumínio são materiais altamente sustentáveis e ecológicos. Eles são leves, reciclável, e energeticamente eficiente, contribuindo para a redução das emissões de carbono e do impacto ambiental em comparação com outros metais. A reciclagem do alumínio requer significativamente menos energia e recursos em comparação com a produção primária, tornando-o uma escolha preferida para soluções de engenharia sustentáveis.
5. Como posso determinar o limite de escoamento de uma liga de alumínio desconhecida?
A resistência ao escoamento de uma liga de alumínio desconhecida pode ser determinada através de métodos de teste padronizados, como testes de tensão ou testes de compressão.. Submetendo o material a cargas controladas e analisando seu comportamento de deformação, os engenheiros podem avaliar com precisão seu limite de escoamento e propriedades mecânicas. Alternativamente, consultar especialistas em materiais ou realizar testes de laboratório pode fornecer informações valiosas sobre o limite de escoamento de ligas de alumínio desconhecidas.


















