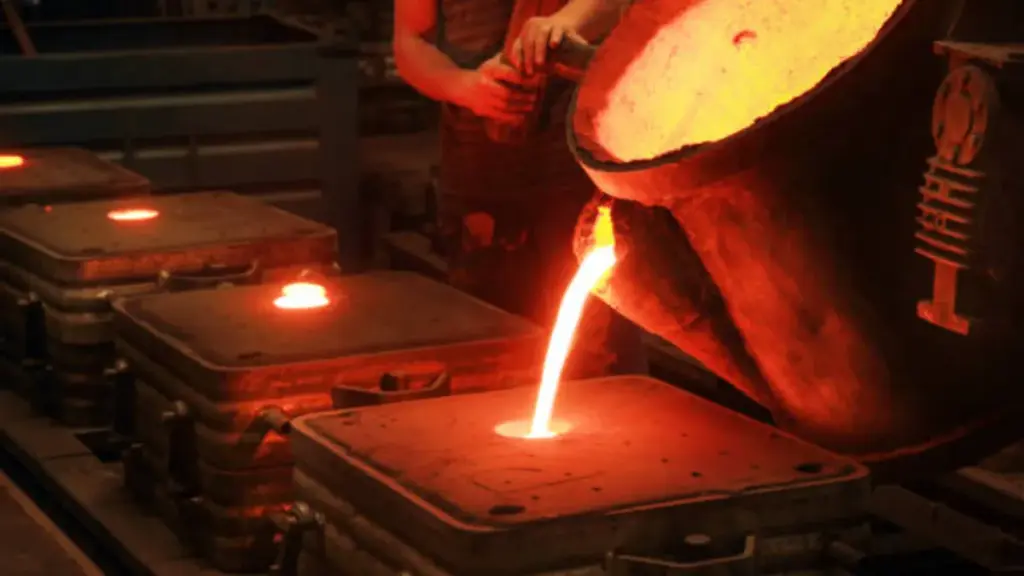
Die casting is a popular manufacturing process that involves injecting molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. This results in precise and complex metal parts that can be used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Two common methods of die casting are hot chamber and cold chamber die casting. In this article, we will compare the two methods and explore their pros and cons to help you determine the best option for your manufacturing needs.
Hot Chamber vs. Cold Chamber Die Casting
The choice between hot chamber die casting vs. cold chamber die casting can make a significant impact on your manufacturing process. In this chapter, let’s delve into their differences in process, cost, efficiency, alloy compatibility, quality control, and environmental impact.
| Aspect | Hot Chamber Die Casting | Cold Chamber Die Casting |
| Process | Molten metal in machine, direct injection into mold | Metal melted externally, then injected into mold |
| Cost | Requires lower initial investment | Higher initial equipment costs |
| Efficiency | Faster cycle times | Slower cycle times |
| Alloy Compatibility | Low melting point alloys (e.g., zinc, magnesium) | High melting point alloys (e.g., aluminum, copper) |
| Quality Control | Limited to simpler parts, may have decreased control over complex geometries | Better control for intricate and detailed parts |
| Environmental Impact | Energy-efficient process | May require more energy for external melting process |
Die Casting Process Differences
In hot chamber die casting, the molten metal is contained in a furnace within the die casting machine itself, allowing for quick and direct injection into the mold cavity.
While in cold chamber die casting, the metal is melted in a separate furnace external to the die casting machine and then transferred into the injection chamber for casting.
Cost comparison
When it comes to cost, hot chamber die casting generally requires lower initial investment compared to cold chamber die casting. This is because hot chamber die casting machines are typically smaller and less complex, making them more affordable for manufacturers. However, operating costs for hot chamber die casting may be higher due to the continuous heating of the metal in the chamber.
Production efficiency
In terms of production efficiency, hot chamber die casting offers faster cycle times compared to cold chamber die casting. This is because the molten metal is already in the chamber, allowing for quicker injection into the mold cavity. Additionally, hot chamber die casting consumes less energy, making it a more efficient option for high-volume production.
Alloy compatibility
Hot chamber die casting is limited to low melting point alloys, such as zinc and magnesium, due to the continuous exposure of the metal to the chamber’s heating element. On the other hand, cold chamber die casting can accommodate high melting point alloys, like aluminum and copper, making it a versatile option for aluminum die casting and a wider range of applications.
Quality control
When it comes to quality control, hot chamber die casting may offer better surface finish due to the rapid cooling of the metal in the mold cavity. However, hot chamber die casting is more prone to porosity, which can affect the structural integrity of the final product. Cold chamber die casting, on the other hand, provides better control over the casting process, resulting in fewer defects and higher quality parts.
Environmental impact
In terms of environmental impact, cold chamber die casting is considered to be more environmentally friendly compared to hot chamber die casting. This is because cold chamber die casting consumes less energy and produces less waste during the manufacturing process. Additionally, cold chamber die casting can be easily integrated with recycling programs, making it a sustainable option for manufacturers.
What is Die Casting?
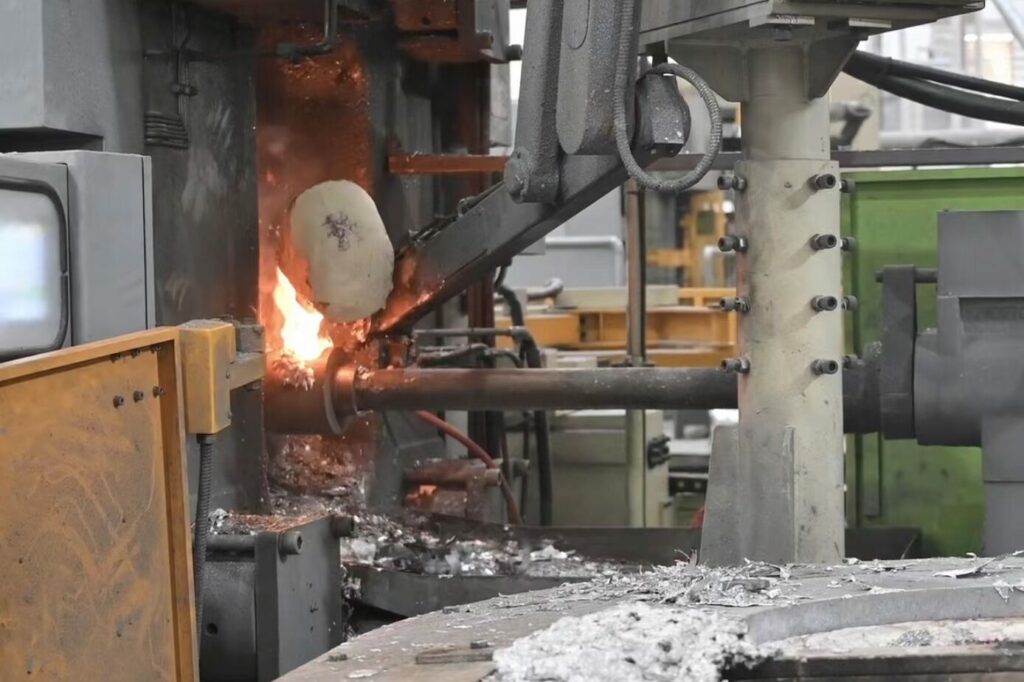

Die casting is a metal casting process that involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. This results in precise and complex metal parts that can be used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Die casting offers a cost-effective and efficient way to produce high-quality metal parts with tight tolerances and excellent surface finish. To learn more, see our guide on die casting.
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Hot chamber die casting is a versatile manufacturing process that offers numerous advantages for producing high-quality metal parts efficiently. By diving into the specifics of hot chamber die casting, we can explore its benefits, limitations, and applications in greater detail.
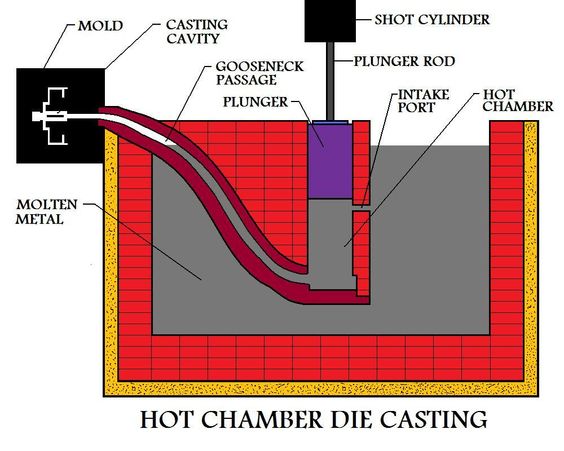
What is Hot Chamber Die Casting?
Hot chamber die casting is a process that involves injecting molten metal, such as zinc or magnesium, into a mold cavity under high pressure. The molten metal is kept in a heated chamber, allowing for quick injection into the mold cavity. Hot chamber die casting is ideal for high-volume production of small to medium-sized parts that require intricate designs and fine details.
Hot Chamber Die Casting Process
The hot chamber die casting process involves 5 key steps to produce high-quality metal parts efficiently. Here is a brief overview of the process:
- Mold Preparation: The first step in hot chamber die casting is preparing the mold cavity, which determines the shape and design of the final metal part.
- Molten Metal Injection: The next step involves melting the metal, typically a low melting point alloy like zinc or magnesium, in a furnace within the hot chamber machine. The molten metal is then injected into the mold cavity under high pressure.
- Cooling and Solidification: Once the molten metal fills the mold cavity, it is left to cool and solidify, taking on the shape of the mold.
- Ejection of the Casting: After the metal has solidified, the casting is ejected from the mold cavity, revealing a precise and detailed metal component.
- Trimming and Finishing: The final step involves trimming any excess material from the casting and performing any necessary finishing processes, such as polishing or surface treatment, to achieve the desired quality and appearance of the metal part.
Overall, hot chamber die casting is a fast and efficient process for mass-producing metal parts with complex geometries and high precision.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hot Chamber Die Casting
Advantages of Hot Chamber Die Casting
- Faster cycle times: Hot chamber die casting boasts swift cycle times, ensuring efficient production processes and quicker turnaround for metal parts.
- Lower energy consumption: This method consumes less energy, contributing to cost savings and environmental sustainability during manufacturing operations.
- Ideal for high-volume production: Hot chamber die casting excels in handling large production volumes, making it a preferred choice for businesses requiring mass outputs of metal components.
Disadvantages of Hot Chamber Die Casting
- Limited to low melting point alloys: One drawback of hot chamber die casting is its limitation to low melting point alloys like zinc and magnesium. This constraint hinders the use of high melting point metals in the manufacturing process.
- Higher maintenance costs: Hot chamber die casting equipment leads to higher maintenance costs for manufacturers due to continuous operation and the need for frequent upkeep to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What Types of Metals are Used for Hot Chamber Casting?
Hot chamber die casting is commonly used for low melting point alloys, such as zinc, magnesium, and lead. These metals offer excellent flowability and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for intricate designs and complex parts. Manufacturers often choose zinc for its high dimensional accuracy and good surface finish, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
Cold Chamber Die Casting
Cold chamber die casting is a precision-driven method that caters to the production of robust metal components. In this chapter, let’s find out everything you need to know about cold chamber die casting.
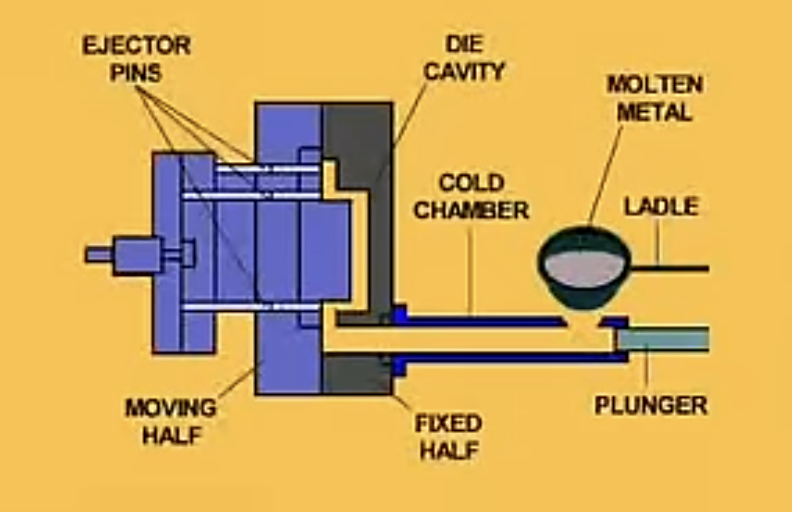
What is Cold Chamber Die Casting?
Cold chamber die casting is a process that involves injecting molten metal, such as aluminum or copper, into a mold cavity under high pressure. Unlike hot chamber die casting, the molten metal is kept in a separate furnace and then transferred to the injection chamber, allowing for better control over the casting process. Cold chamber die casting is suitable for high melting point alloys that require precise and durable parts.
Cold Chamber Die Casting Process
The cold chamber die casting process is a meticulous method used to manufacture high-quality metal components, particularly those requiring high melting point alloys such as aluminum and copper. Here is a brief overview of the cold chamber die casting process:
- Mold Preparation: The process begins with the preparation of a mold cavity that corresponds to the desired shape and details of the metal part to be produced.
- Metal Melting: Unlike hot chamber die casting, the cold chamber process involves melting the metal, typically aluminum or copper, in a separate furnace external to the die casting machine.
- Injection of Molten Metal: Once the metal is molten, it is ladled or transferred into the cold chamber of the die casting machine. The molten metal is then injected into the mold cavity under high pressure to ensure precise filling and solidification.
- Cooling and Solidification: The molten metal cools and solidifies within the mold cavity, taking on the shape and characteristics of the mold to form the final metal part.
- Ejection and Removal: After the metal has solidified, the casting is ejected from the mold cavity, revealing the detailed and durable metal component within.
- Trim and Finish: Any excess material or imperfections on the casting are trimmed away, and additional finishing processes, such as deburring, polishing, or coating, may be applied to achieve the desired quality and surface finish of the metal part.
The cold chamber die casting process enables the production of robust and precise metal components, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring strong and durable metal parts made from high melting point alloys.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cold Chamber Die Casting
Advantages of Cold Chamber Die Casting
- Suitable for high melting point alloys: Cold chamber die casting accommodates high melting point alloys such as aluminum and copper, expanding the versatility and range of metal options for precision manufacturing.
- Better control over casting process: This method offers superior control during the casting process, enabling manufacturers to produce intricate and high-quality metal components with precision and consistency.
- Longer die life: Cold chamber die casting typically results in a longer die life compared to other methods, minimizing the need for frequent die replacements and optimizing production efficiency.
Disadvantages of Cold Chamber Die Casting
- Slower cycle times: One drawback of cold chamber die casting is its slower cycle times compared to hot chamber die casting, as the process involves transferring molten metal from a separate furnace before injection into the mold cavity.
- Higher initial costs: Cold chamber die casting equipment often requires larger and more complex machinery, leading to higher initial investment costs for manufacturers. Despite its benefits, the upfront expenses may pose a financial challenge for some businesses.
What Types of Metals are Used for Cold Chamber Casting?
Cold chamber die casting is commonly used for high melting point alloys, such as aluminum, copper, and brass. These metals offer excellent strength, durability, and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for applications that require precise and durable parts. Manufacturers often choose aluminum for its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for automotive parts and aerospace components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both hot chamber and cold chamber die casting offer unique advantages and disadvantages that cater to different manufacturing needs. Hot chamber die casting is ideal for low melting point alloys and high-volume production, while cold chamber die casting is suitable for high melting point alloys and better control over the casting process. Ultimately, the choice between hot chamber and cold chamber die casting depends on factors such as the type of metal alloy, production volume, and quality requirements.


















