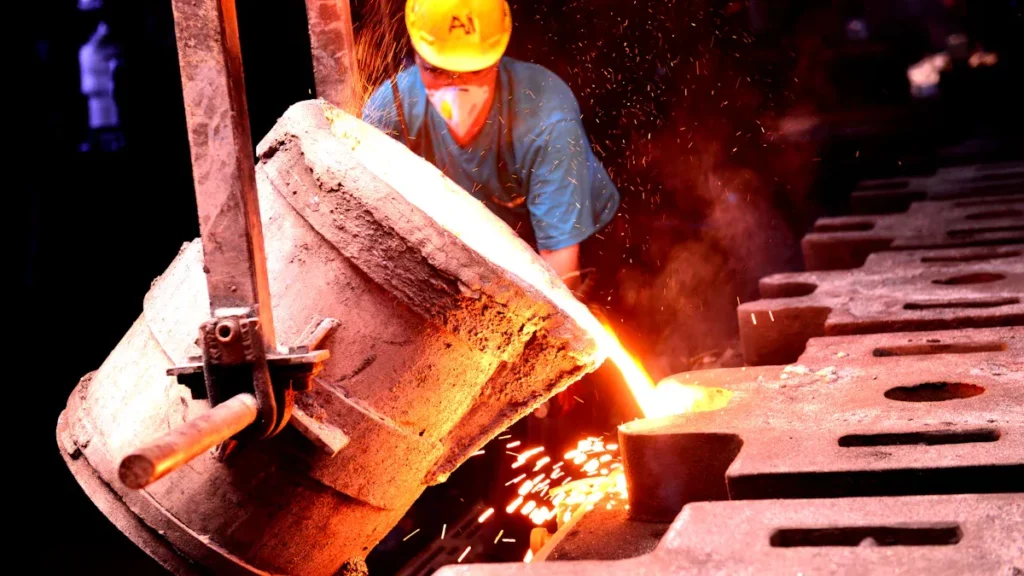
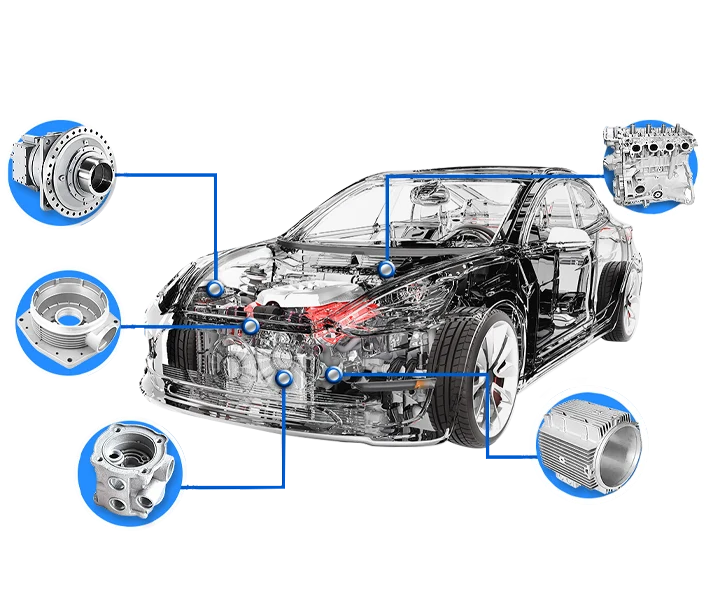
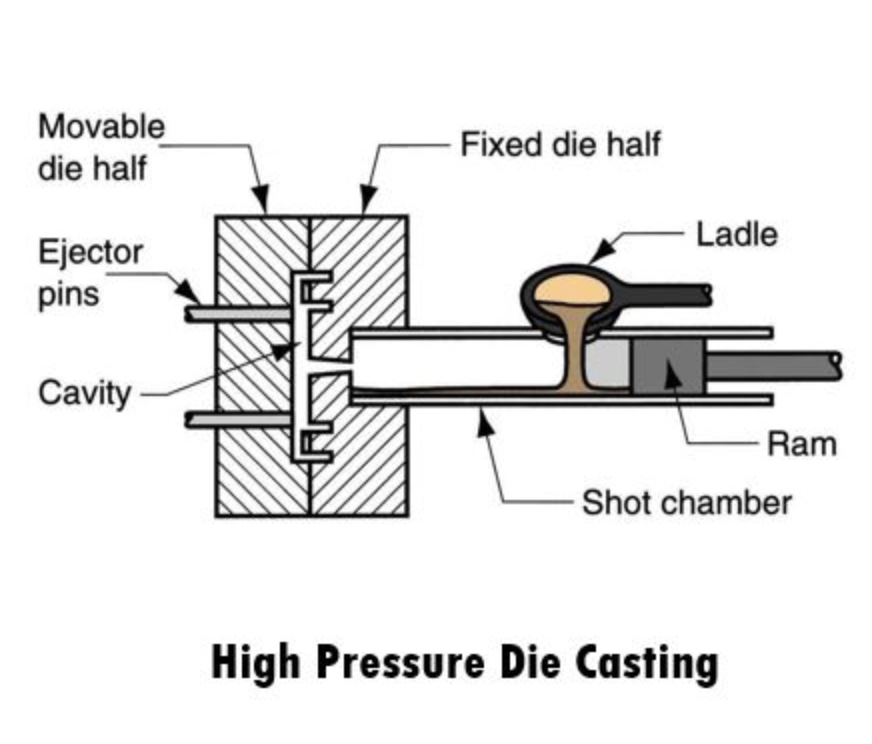
Die casting is a widely used manufacturing process that involves the production of metal parts by forcing molten metal into a mold cavity using high pressure. It is a versatile and cost-effective method that allows for the production of complex shapes with tight tolerances. This article will explore the basics of die casting, the materials used, various die casting processes, and its applications across industries.
What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten metal into a mold cavity at high pressure, so traditional die casting is aslo called high-pressure die casting. The metal is then cooled and solidified, resulting in a cast component that closely matches the shape and dimensions of the mold. This process is suitable for producing high-volume, complex parts with excellent dimensional accuracy.
Compared to other manufacturing methods like sand casting or investment casting, die casting offers several advantages. It allows for the production of parts with thin walls and intricate details, reducing the need for further machining. Additionally, die casting has a higher production rate, lower labor costs, and can achieve tighter tolerances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting
Advantages of Die Casting
- High productivity: Die casting can produce a large number of parts quickly, resulting in time and cost savings.
- Dimensional accuracy: Parts made through die casting closely replicate desired specifications, reducing the need for additional machining.
- Cost-effective solution: Die casting minimizes labor costs and post-processing requirements, providing long-term cost savings.
- Complex geometry: Die casting enables the production of intricate designs and complex parts.
Disadvantages of Die Casting
- High initial tooling cost: Creating molds for die casting can be expensive, especially for small-scale production.
- Size limitations: Die casting is more suitable for smaller to medium-sized parts.
- Limited mold life: Repeated high-pressure injection can lead to wear and tear on molds, requiring replacement or repair.
- Restricted material selection: Die casting may have limitations on material choices compared to other methods.
Materials Used in Die Casting
Die casting can be performed with a variety of metals and alloys, including aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Each alloy offers unique properties and advantages, making them suitable for different applications.
Aluminum Die Casting

Aluminum is one of the most commonly used metals for die casting due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It is lightweight, yet durable, making it ideal for automotive components, electronic enclosures, and consumer goods.
Aluminum die casting offers several advantages, such as high thermal conductivity, good machinability, and excellent dimensional stability. It also allows for the production of thin-walled parts with complex shapes, reducing the need for additional machining operations.
Zinc Die Casting

Zinc is another popular choice for die casting, known for its excellent casting properties and low melting point. It is commonly used in the production of electrical connectors, decorative hardware, and automotive components.
Zinc die casting offers excellent fluidity and precise castability, allowing for the production of intricate and thin-walled parts. It also provides good corrosion resistance and excellent surface finish, making it a cost-effective option for many applications.
Brass Die Casting

Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is widely used in die casting due to its unique properties. Brass die castings offer excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties, and high machinability. They are commonly employed in various applications that require both aesthetic appeal and functional properties. Some common applications of brass die castings include plumbing fixtures, decorative hardware, electrical connectors, and musical instruments.
Magnesium Die Casting
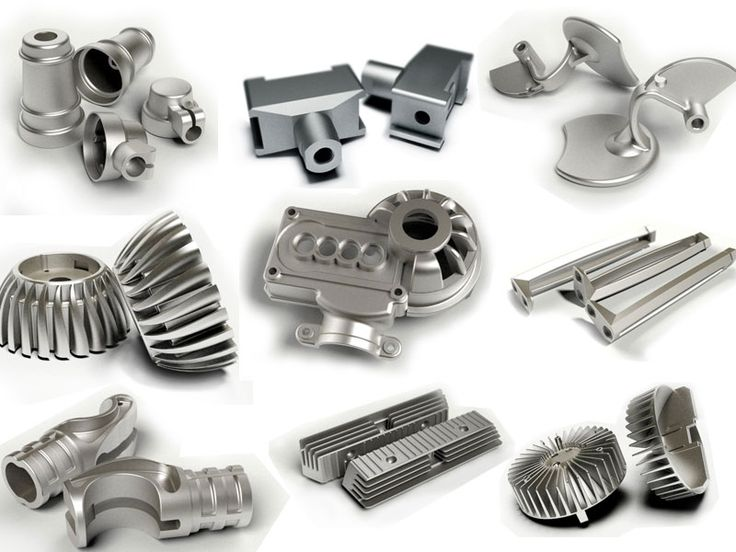

Magnesium is a lightweight metal with excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial. It is often used in the aerospace industry, automotive components, and electronic devices.
Magnesium die casting offers exceptional dimensional stability, high thermal conductivity, and excellent electromagnetic shielding properties. It also provides strong resistance to corrosion and is easily recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
3 Types of Die Casting Processes
Certainly! Here’s a comparison table for Cold chamber die casting, Hot chamber die casting, and Vacuum die casting:
| Cold Chamber Die Casting | Hot Chamber Die Casting | Vacuum Die Casting | |
| Suitable Materials | Aluminum, magnesium, copper, various alloys | Zinc, lead, tin alloys | Aluminum, magnesium, copper, various alloys |
| Operation Method | Molten metal is ladled from a separate furnace | Molten metal is pumped directly into the mold | Molten metal is poured into a sealed chamber |
| Process Temperature | Higher temperature | Lower temperature (near the melting point) | Lower temperature (below the melting point) |
| Complexity of Parts Produced | Able to produce more complex parts with thicker walls | Suits simpler and smaller parts | Suitable for complex parts |
| Cost of Equipment | Costlier equipment setup required | Less expensive equipment setup required | Moderate equipment setup required |
| Uses in Industries | Automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, electronics, etc. | Small household appliances, plumbing components, etc. | Aerospace, automotive, medical, electronic devices, etc. |
Please note that the table above is a general comparison and may not cover every aspect of eac
Cold Chamber Die Casting
What is cold chamber die casting? In cold chamber die casting, the molten metal is poured into a separate chamber and then injected into the mold cavity using a plunger. This method is suitable for alloys with high melting points, such as aluminum and copper.
Cold chamber die casting is commonly used in the production of automotive components, aerospace parts, and larger castings that require high pressure.
Hot Chamber Die Casting
What is hot chamber die casting? Hot chamber die casting is a process where the injection mechanism is integrated into the furnace. The molten metal is continuously supplied, eliminating the need for a separate chamber. This method is suitable for alloys with low melting points, such as zinc and magnesium.
Hot chamber die casting is often employed in the production of smaller, intricate parts, such as electronic connectors, small automotive components, and household appliances.
Vacuum Die Casting
Vacuum die casting is a variation of the traditional die casting process where a vacuum is applied during the injection stage. This helps to remove trapped gases and reduce porosity in the final castings, resulting in improved mechanical properties.
Vacuum die casting is widely used in industries where high-quality, defect-free castings are critical, such as aerospace, medical, and precision engineering.
The Process of Die Casting
Step #1: Mold Design
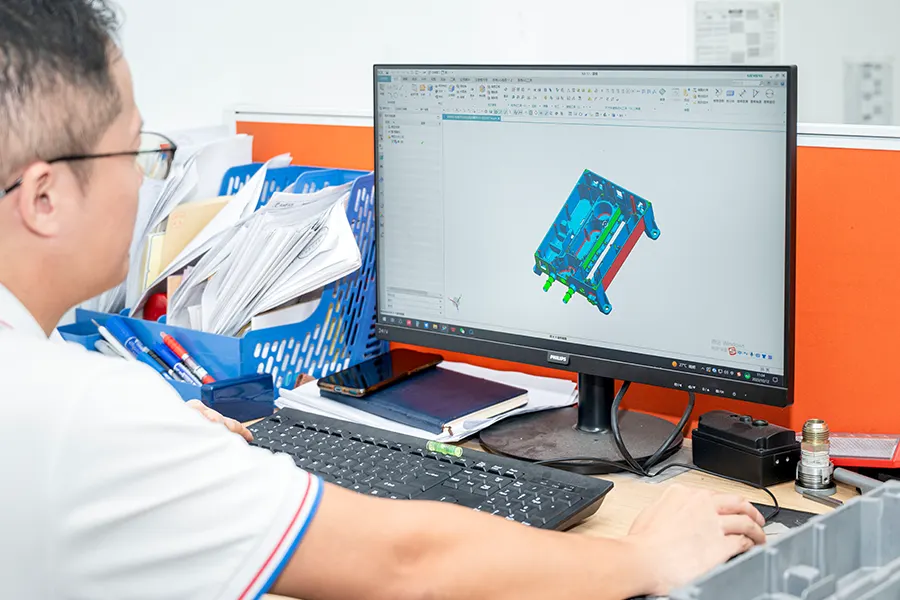

The first step in the die casting process is the design and fabrication of the mold. The mold must be designed to withstand high pressure and temperature while maintaining the desired shape and dimensions of the final part.
Step #2: Casting Preparation
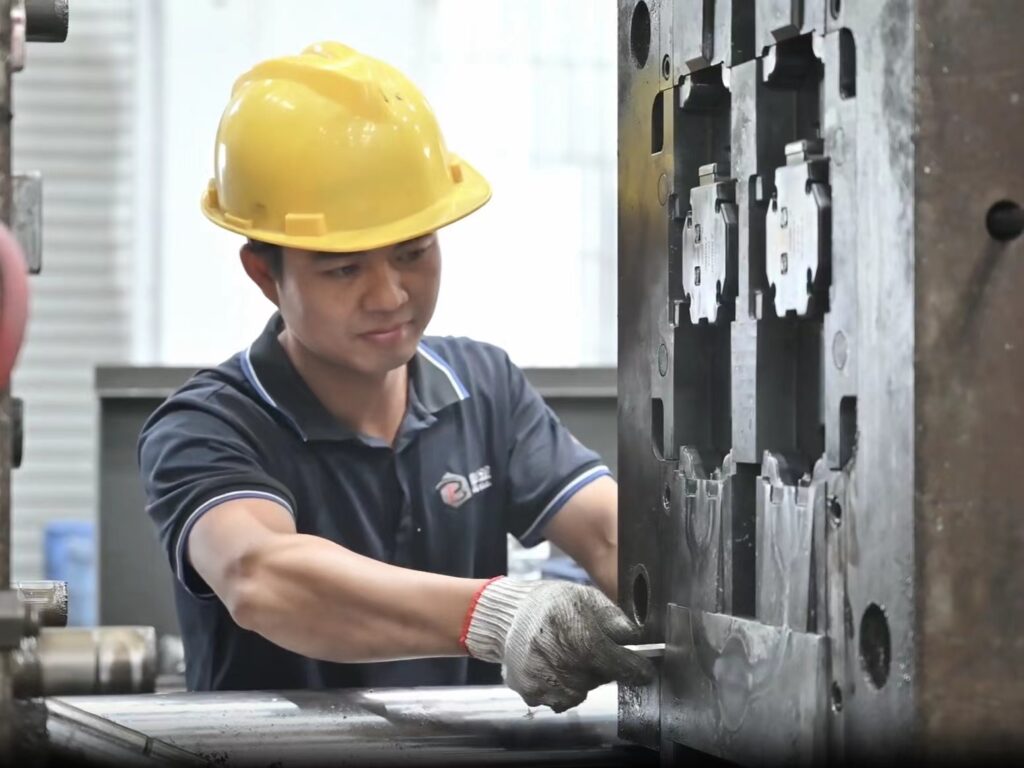

Once the mold is ready, it is preheated to the desired temperature to ensure proper heat transfer during the casting process. Any necessary release agents or coatings are applied to the mold to prevent sticking and facilitate part removal.
Step #3: Injection
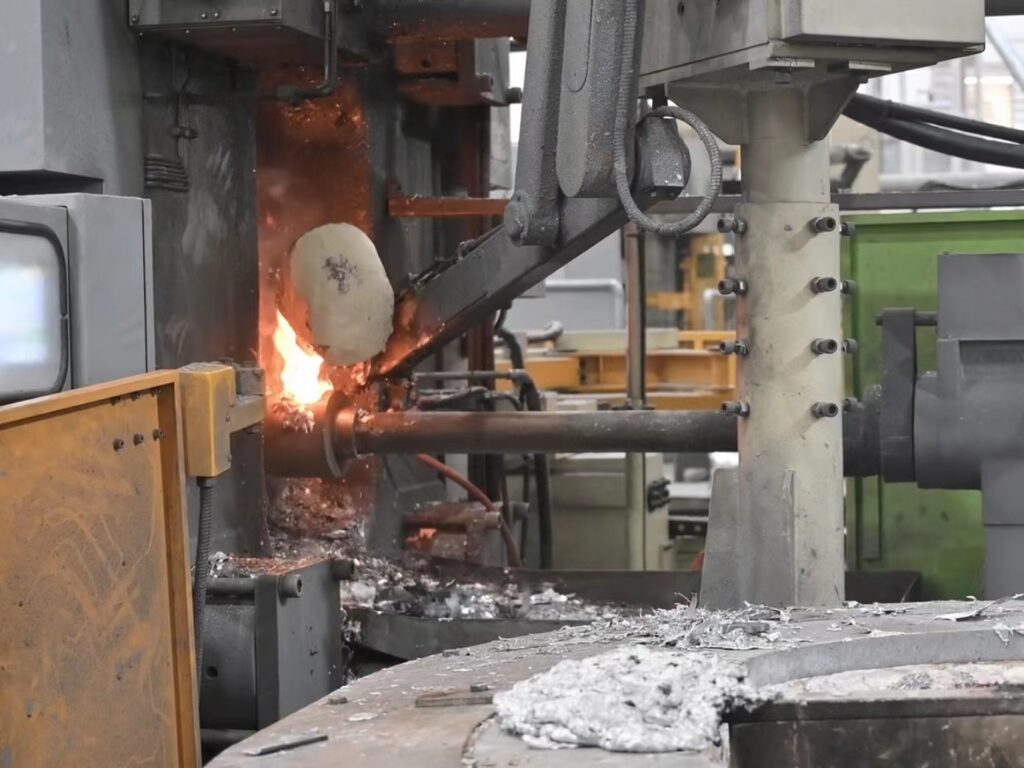

The molten metal is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure using a plunger or a hydraulic piston. The high pressure helps to fill the mold completely and ensures good dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Step #4: Cooling and solidification
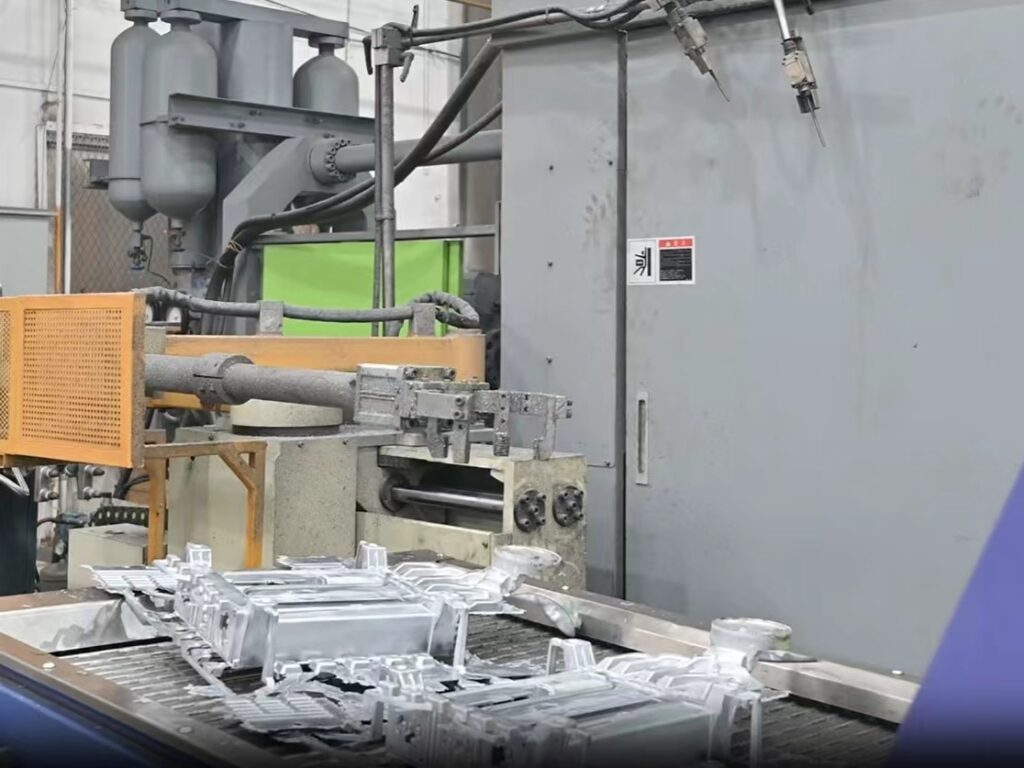

After injection, the molten metal is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold cavity. The cooling time varies depending on the material and part geometry, but it is crucial to control the cooling rate to prevent defects like shrinkage or porosity.
Step #5: Demolding / Removal
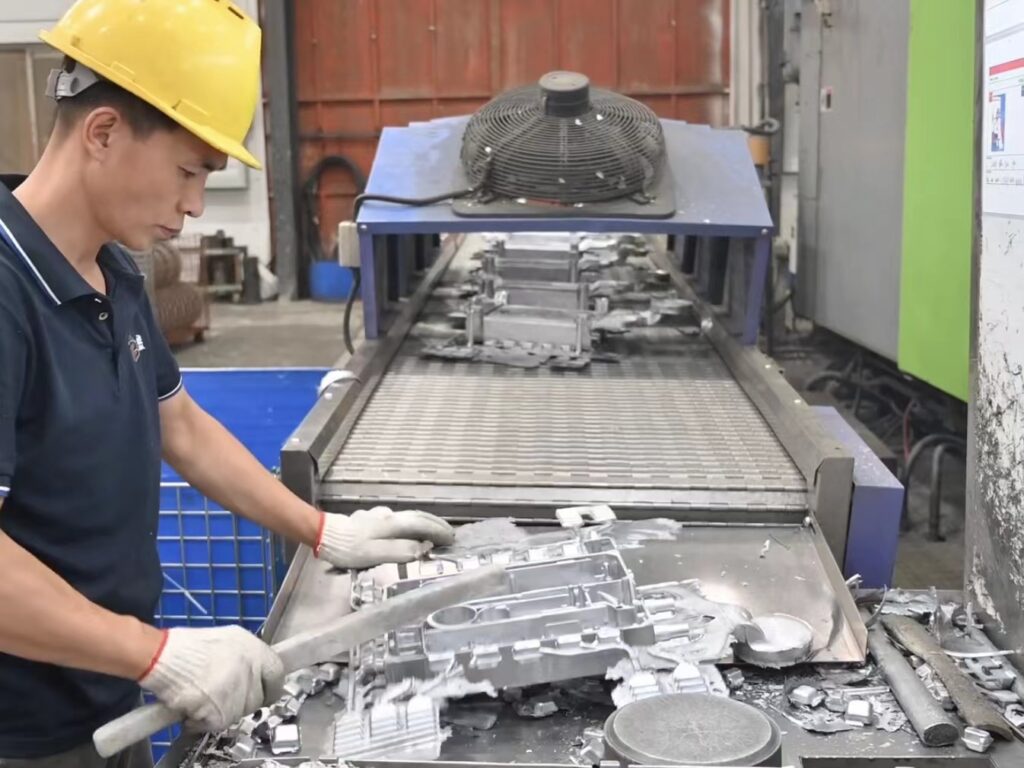

Once the part has solidified, the mold is opened, and the casting is removed. Care must be taken to prevent any damage to the part during demolding.
Step #6: CNC machining / Surface Treatment
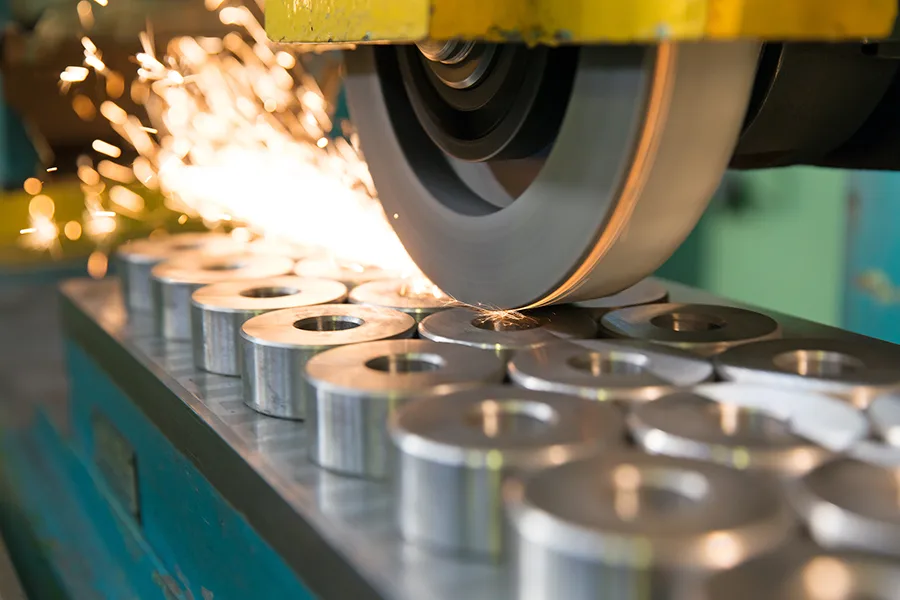

In some cases, additional machining operations may be required to achieve the desired shape, dimensions, or surface finish. This can be done using CNC machining, drilling, tapping, or other post-processing techniques. Surface treatments like plating, painting, or powder coating may also be applied to enhance the appearance and corrosion resistance of the part.
Die Casting Applications Across Industries

Automotive Industry
Die casting plays a vital role in the automotive industry by providing lightweight yet durable parts like engine components, transmission housings, and body components. It helps to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance overall vehicle performance.
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, die casting is used to produce critical components that require high strength, dimensional accuracy, and lightweight properties. Parts like turbine blades, aircraft structural components, and engine housings are commonly manufactured through the die casting process.
Electronics and Telecommunications Industry
Die casting is widely employed in the electronics and telecommunications industry to produce components like connectors, housings, and heat sinks. The process allows for intricate designs, excellent heat dissipation, and electromagnetic shielding properties.
Consumer Goods and Appliances
Many consumer goods and appliances rely on die casting for the production of various components. From kitchen appliances to power tools, die casting provides the durability, strength, and precise dimensions required for these products.
Medical and Healthcare Sector
The medical and healthcare sector utilizes die casting for the production of surgical instruments, medical devices, and equipment components. Die casting offers the necessary accuracy, cleanliness, and sterilizability required in this industry.
Conclusion
Die casting is a versatile and widely used manufacturing process that allows for the production of complex and high-quality metal parts. Understanding the basics of die casting, the materials used, various die casting processes, and its applications across industries is essential for anyone involved in the manufacturing or engineering field. By leveraging the advantages and capabilities of die casting, manufacturers can produce parts that meet the demanding requirements of today’s industries.
FAQs
1. What is flash in die casting?
Flash in die casting refers to excess material that is squeezed out between the two halves of the die during the casting process, creating unwanted protrusions on the casting surface.
2. What is gravity die casting?
Gravity die casting, or permanent mold casting, is a casting process where molten metal is poured into a reusable mold using gravity to aid in the filling of the mold cavity, resulting in high-quality castings.
3. What is aluminum die casting?
Aluminum die casting is a process that uses molten aluminum alloy injected into a mold cavity at high pressure to produce precise and lightweight castings for various industries.
4. What is mold casting?
Mold casting is a broad term encompassing casting processes that utilize molds to shape and solidify molten materials like metal or plastic into the desired form.
5. What is die casting used for?
Die casting is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics to produce complex and high-quality metal components with excellent dimensional accuracy at a fast production rate.
6. What are the most common metals used in die casting?
The most common metals used in die casting are aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. These metals offer excellent properties for the die casting process, such as good flowability, thermal conductivity, and strength-to-weight ratio. Other metals, including brass and copper, are also used in die casting, although they are less common than aluminum, zinc, and magnesium.