When it comes to comparing materials, cast iron and cast aluminium stand out due to their unique characteristics and diverse applications. While both materials have their respective strengths and weaknesses, understanding their differences is crucial for making informed decisions in various contexts. In this article, we will delve into the distinctions between cast iron and cast aluminium, examining factors such as weight, heat retention, and corrosion resistance, etc.
| Factors | Cast Iron | Cast Aluminum |
| Weight | Heavyweight | Lightweight |
| Heat Retention | Excellent heat retention | Less effective heat retention |
| Heat Conductivity | Lower heat conductivity | Higher heat conductivity |
| Corrosion Resistance | Prone to corrosion and rust | Highly corrosion-resistant |
| Durability | Highly durable | Relatively durable |
| Cost | Often more expensive | Generally more affordable |
What Is Cast Aluminum?
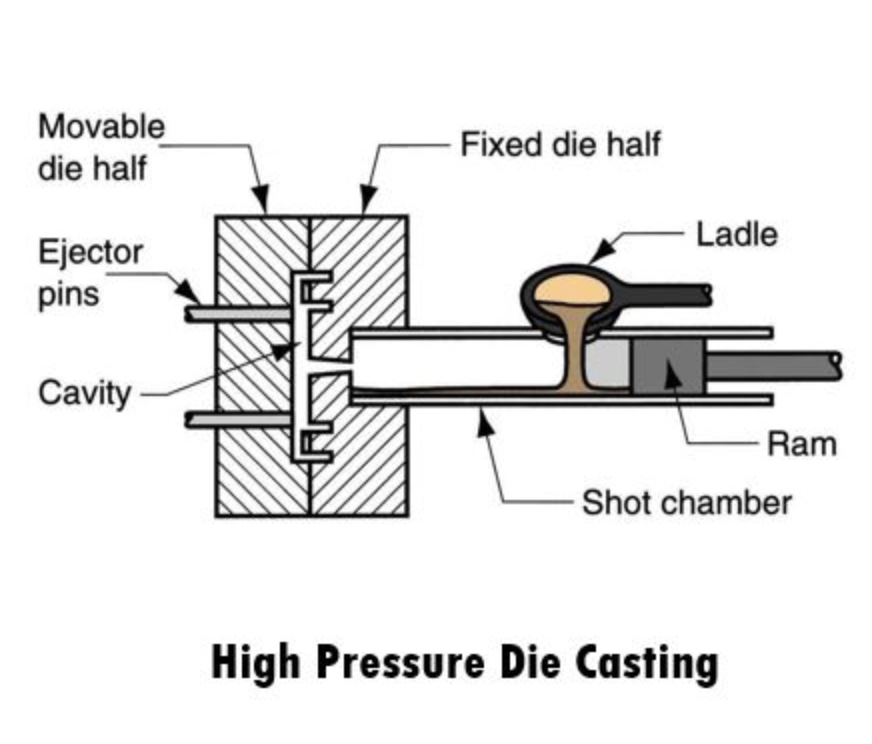
Cast aluminum is a lightweight material formed by pouring molten aluminum alloy into molds, allowing for precise shaping. Its notable trait lies in its fantastic heat conductivity, ensuring even heat distribution during various processes. This makes cast aluminum well-suited for quick and efficient cooking methods, where precise temperature control is crucial.
What Is Cast Iron?
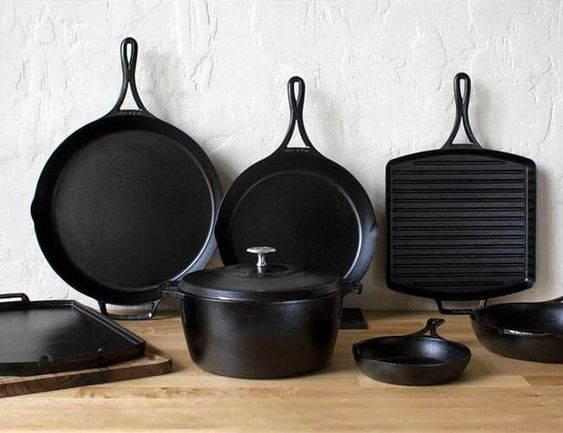

In contrast, cast iron is a robust and heavy material produced by pouring molten iron into molds. Its exceptional heat retention capabilities set it apart, making it ideal for slow and prolonged cooking. The weight of cast iron contributes to its ability to distribute heat evenly, maintaining consistent temperatures throughout the cookware. This makes it perfect for achieving a superb sear and conducting slow-cooking processes effectively.
Cast Iron vs. Cast Aluminum

When it comes to comparing cast iron and cast aluminum, several factors come into play. In order to make an informed decision, it is essential to examine their distinctions in weight, heat retention, heat conductivity, corrosion resistance, durability, and cost. Let’s delve deeper into these aspects:
A. Weight
One of the primary differentiating factors between cast iron and cast aluminum is weight. Cast aluminum is significantly lighter compared to cast iron. This lightweight nature makes cast aluminum more manageable and easier to handle, especially when it comes to larger pieces of cookware. On the other hand, cast iron is notably heavy, which can provide stability during cooking but may also pose challenges for those who prefer lightweight options or have physical limitations.
B. Heat Retention
Heat retention is a crucial consideration when choosing between cast iron and cast aluminum. Cast iron excels in this aspect, as it has impressive heat retention capabilities. It can absorb and distribute heat evenly, ensuring consistent temperatures throughout the cookware. This makes cast iron ideal for slow-cooking methods and dishes that require prolonged simmering. In contrast, while cast aluminum conducts heat well, it does not retain heat as effectively as cast iron. This property might be suitable for quick-cooking methods but may be less suitable for dishes that demand sustained heat over an extended period.
C. Heat Conductivity
Along with heat retention, heat conductivity is another important factor to consider. Cast aluminum outshines cast iron in terms of heat conductivity. It conducts heat quickly and evenly across the surface, ensuring efficient and precise cooking. This property is especially advantageous when it comes to achieving uniform browning and reducing the risk of unevenly cooked food. Cast iron, although capable of distributing heat evenly once it is heated, may require more time to reach an even temperature due to its lower conductivity.
D. Corrosion Resistance
When it comes to corrosion resistance, cast aluminum has the upper hand. Aluminum naturally forms a protective layer of oxide, which acts as a barrier against corrosion. This characteristic makes cast aluminum highly resistant to rust and other forms of degradation, ensuring its longevity. In comparison, cast iron is more prone to corrosion and rust, especially if not properly seasoned and maintained. Regular seasoning and proper care are essential to prevent the formation of rust and extend the lifespan of cast iron cookware.
E. Durability
In terms of durability, both cast iron and cast aluminum have distinct advantages. Cast iron is renowned for its exceptional durability, with many cast iron cookware pieces lasting for generations when properly cared for. Its solid construction and resistance to impact make it highly durable. Cast aluminum, while not as durable as cast iron, still offers good durability, particularly when it comes to lightweight applications. However, it is important to handle cast aluminum cookware with care to prevent dents and scratches that can affect its longevity.
F. Cost
Cost is often a significant consideration when making a purchase decision. Cast aluminum generally tends to be more affordable compared to cast iron. The production process for cast aluminum is less labor-intensive, resulting in a lower price point. In contrast, cast iron cookware is often more expensive due to the higher cost of production. However, it is worth noting that the longevity and durability of cast iron can offset the initial investment, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Pros and Cons of Cast Aluminum
Cast aluminum offers several advantages, making it popular among different industries.
Pros
- High heat conductivity for quick and uniform cooking.
- Non-stick surface for easier cooking and cleaning.
- Lightweight and practical for transportation.
- Corrosion-resistant and durable.
Cons
- Susceptible to scratches and dents, requiring careful handling and maintenance.
- Limited heat retention, less suitable for long-simmered dishes.
Pros and Cons of Cast Iron
The following are the pros and cons of cast iron.
Pros
- Unparalleled heat retention for optimal slow-cooking processes.
- Natural development of non-stick surface over time enhances versatility and ease of use.
- Durability and resistance to scratching, making it compatible with metal utensils.
Cons
- Heavyweight may hinder ease of handling and maneuverability.
- Extra care required for cleaning and pouring liquids due to its weight.
- Regular seasoning and maintenance necessary to prevent rusting.
Cast Aluminium vs. Cast Iron, Which Is Better?
Choosing between cast aluminium and cast iron ultimately boils down to personal preference and specific requirements.
Cast aluminum is an excellent choice when considering lightweight convenience and efficient heat conductivity. It excels in applications that prioritize quick cooking and precise temperature control.
On the other hand, cast iron shines in terms of heat retention and durability. Its heavyweight nature ensures excellent heat distribution and makes it ideal for long cooking processes and achieving exceptional searing results. However, the weight and maintenance demands of cast iron may not suit everyone’s needs.
Conclusion
Both cast iron and cast aluminium possess distinct characteristics that suit different purposes. Cast aluminum’s lightweight nature and efficient heat conductivity make it an excellent choice for quick and precise cooking. Meanwhile, cast iron’s remarkable heat retention abilities and durability lend themselves to slow-cooking methods and achieving exceptional searing results. By understanding the differences between cast iron and cast aluminium, you can make informed decisions when selecting materials for various applications.
FAQs
- Does cast aluminum rust?
No, cast aluminum does not rust. It naturally forms a protective layer of oxide, which acts as a barrier against corrosion and rust.
- Is cast iron brittle?
No, cast iron is not considered brittle. It is a strong and durable material known for its impact resistance. However, it can be susceptible to cracking if subjected to sudden and extreme temperature changes.
3. How to tell cast iron from steel?
One way to differentiate between cast iron and steel is through a simple magnet test. Cast iron is highly magnetic, while steel may exhibit only slight magnetic properties or none at all. Additionally, cast iron typically has a rougher and more textured surface compared to the smoother surface of steel.
- How to tell if something is cast iron?
To determine if something is cast iron, you can look for a few key characteristics. Cast iron is typically heavy, often exhibiting a rough texture or visible casting marks on its surface. It is not magnetic, meaning a magnet will not strongly stick to it. Additionally, the presence of a dark, seasoned coating or the ability to develop a non-stick surface over time can be indicative of cast iron.
- How strong is cast aluminum?
Cast aluminum is generally considered to be a strong and durable material. Its strength-to-weight ratio is impressive, making it suitable for various applications. While it may not be as strong as some other metals like steel or cast iron, it offers sufficient strength for everyday use, especially in contexts where its lightweight nature is advantageous.