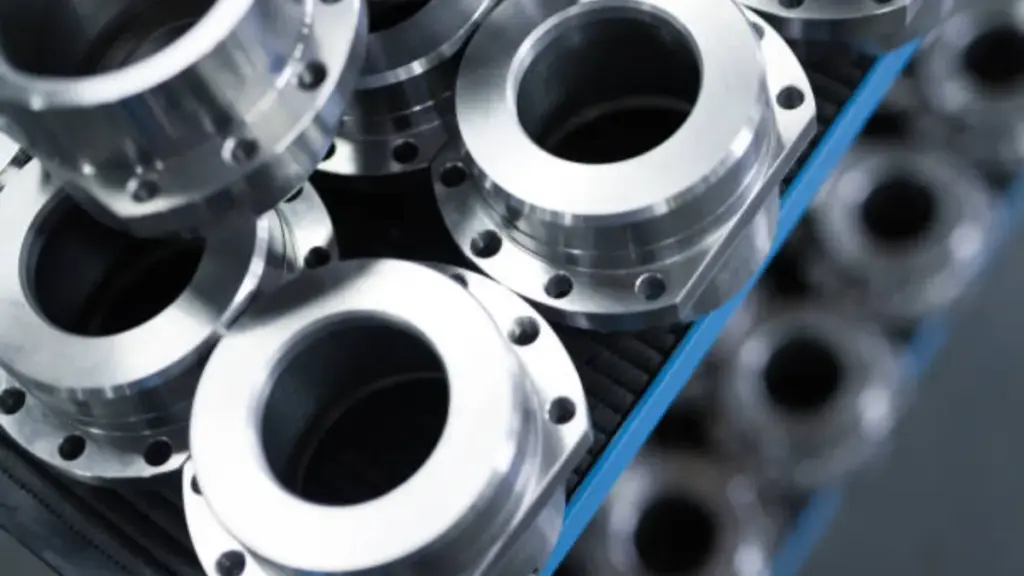
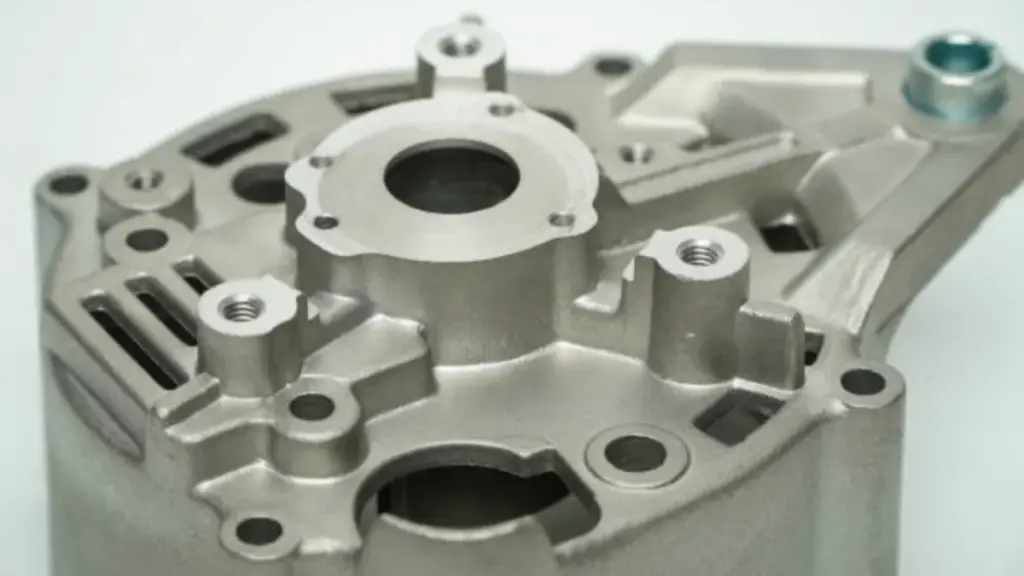
When it comes to manufacturing metal parts, two commonly used processes are die casting and investment casting. Both methods have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand the differences between the two before deciding which process is best suited for a particular project.
What is Die Casting?
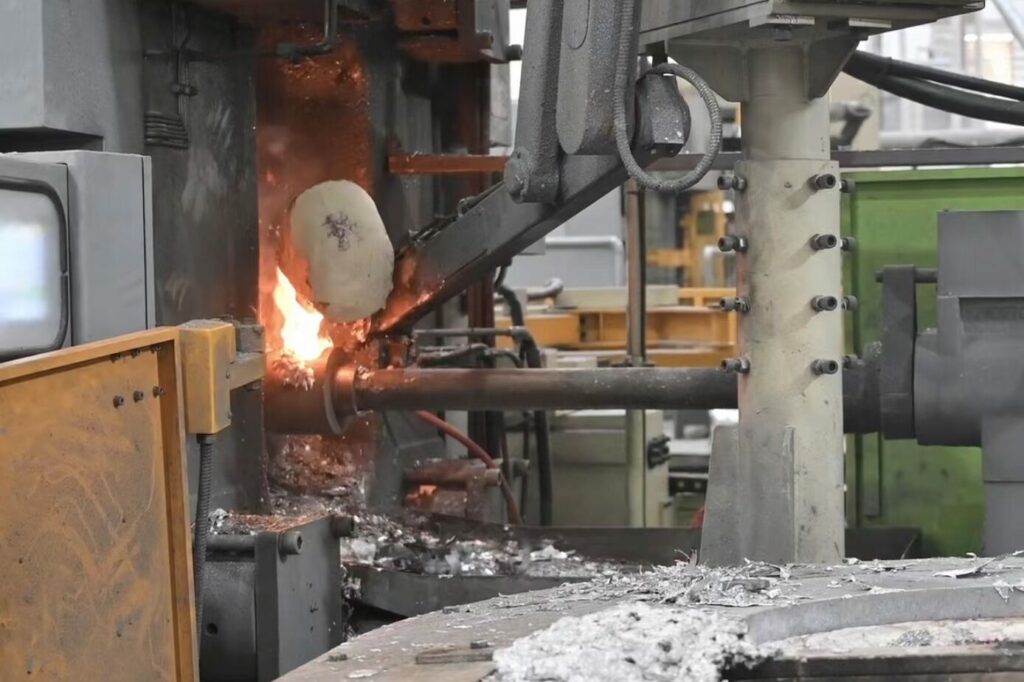

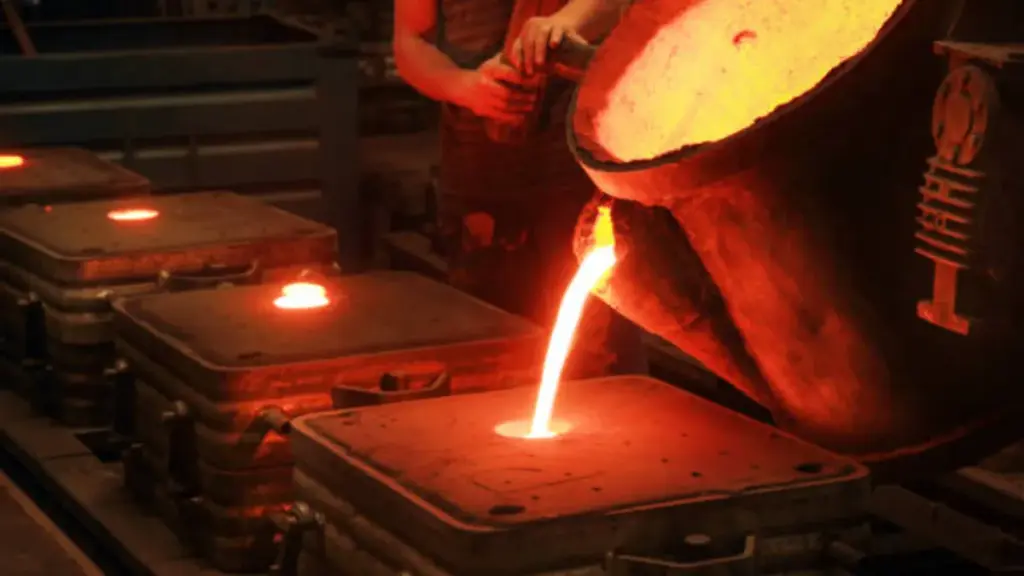
Die casting is a manufacturing process that involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. The metal solidifies quickly, creating a precise and high-quality part. This process is ideal for producing large quantities of parts with consistent quality and surface finish.
What Is Die Casting Process?
The die casting process starts with melting the metal, typically aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, in a furnace. The molten metal is then injected into a steel mold cavity using a high-pressure machine. Once the metal cools and solidifies, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting
Advantages of Die Casting
- Cost-effective for large production runs: Die casting is an efficient process for producing a high volume of parts quickly and cost-effectively.
- Consistent quality and surface finish: Die casting results in parts with uniform dimensions and smooth surfaces, making it an ideal choice for applications that require precision.
- Rapid production for large orders: Die casting is renowned for its efficiency in producing a high volume of parts quickly. This rapid production capability is particularly beneficial for companies looking to fulfill large orders within tight deadlines.
- Complex shapes and intricate designs: Die casting enables the creation of parts with intricate designs and complex shapes that may be challenging to achieve with other manufacturing processes. This versatility makes die casting suitable for a wide range of applications across different industries.
- Tight dimensional tolerances: Die casting offers high precision and tight dimensional tolerances, ensuring that parts meet stringent quality standards. This level of accuracy is essential for industries where precision engineering is critical.
- Wide range of finishing options: Die casting allows for a variety of finishes to be applied to parts, including painting, powder coating, and plating. This versatility in finishing options enables customization and aesthetic enhancement of the final product.
Limitations of Die Casting
- Limited material options: Die casting is typically limited to non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium, limiting the range of materials that can be used.
- High initial tooling costs: The molds used in die casting can be expensive to create, making it less economical for small production runs.
What is Investment Casting?
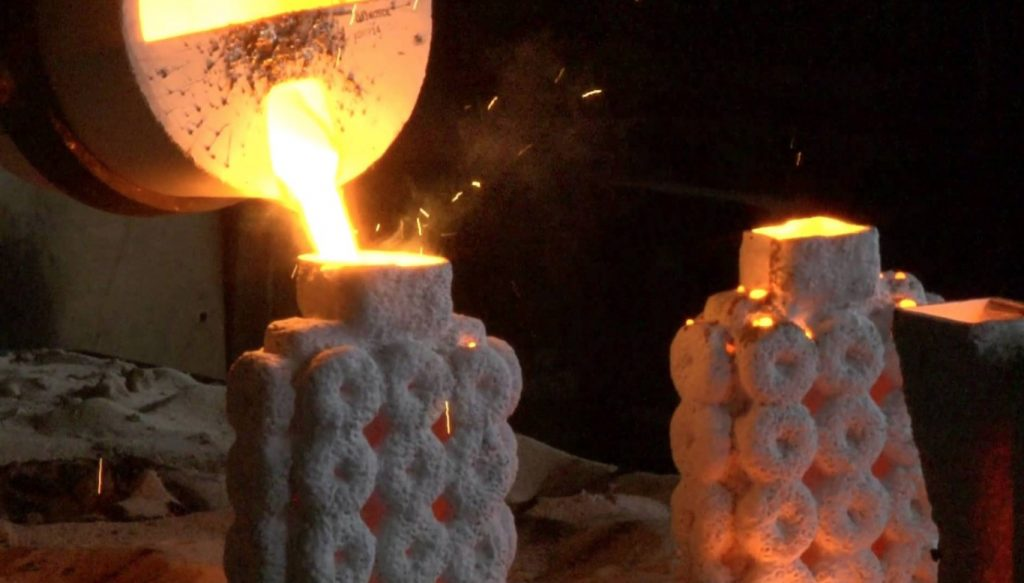

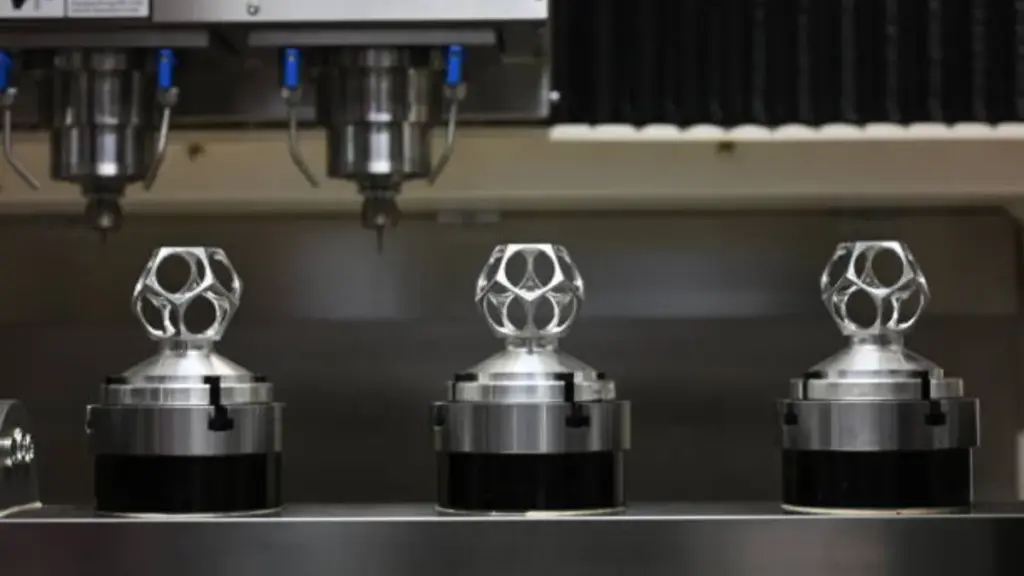
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a manufacturing process that uses a wax pattern to create intricate metal parts. This process is ideal for producing complex shapes with fine details and is widely used in industries such as jewelry and aerospace.
What is Investment Casting Process?
The investment casting process begins with creating a wax pattern of the part to be cast. The wax pattern is coated with a ceramic shell and heated to remove the wax, leaving behind a hollow ceramic mold. Molten metal is then poured into the mold, filling the cavity and forming the final part once the metal cools and solidifies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Investment Casting
Advantages of Investment Casting
- Suitable for intricate and high-detail parts: Investment casting allows for the production of complex parts with fine details that may be challenging to achieve with other manufacturing processes.
- Wide range of materials can be used: Investment casting supports a variety of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium, providing flexibility in material selection.
- Reduction in machining and tooling costs: Investment casting often leads to minimal machining and tooling requirements, as parts are produced near net shape. This reduction in secondary operations lowers overall production costs and enhances efficiency in the manufacturing process.
- Design flexibility: Investment casting offers design flexibility, allowing for the production of parts with complex geometries and unique shapes. This design freedom enables manufacturers to bring innovative concepts to life and meet specific customer demands with tailored solutions.
- Superior strength and durability: Components produced through investment casting display superior strength and durability, making them suitable for applications that require high-performance and reliability. The robust nature of investment cast parts ensures longevity and resilience in challenging operating environments.
Limitations of Investment Casting
- Longer production times: The investment casting process can be time-consuming, with multiple steps involved in creating the final part, resulting in longer lead times.
- More labor-intensive process: Investment casting requires skilled labor to create and assemble the wax patterns and ceramic molds, adding to the overall production costs.
Difference Between Die Casting and Investment Casting
Tolerance and Surface Finish
- Die Casting provides tighter tolerances and smoother surfaces due to the high pressure used in the process.
- nvestment Casting allows for greater design flexibility and finer details, making it suitable for complex and intricate parts.
Cost Considerations
- Die Casting is more cost-effective for high volume production runs, as the initial tooling costs can be spread out over a larger number of parts.
- Investment Casting is preferred for lower volume production or parts with complex geometries that may be difficult to achieve with other methods.
Material Options
- Die Casting is typically limited to non-ferrous metals such as aluminum and zinc, restricting the range of materials that can be used.
- Investment Casting supports a wide variety of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium, providing greater flexibility in material selection.
Applications
- Industries that benefit from Die Casting include automotive parts die casting, aerospace, and consumer electronics, where high volume production and precision are essential.
- Industries that benefit from Investment Casting include jewelry, medical equipment, and military applications, where complex shapes and fine details are required.
Which Process Is Suitable for Your Project?

When choosing between die casting and investment casting for a project, several factors need to be considered:
- Production volume: Die casting is ideal for high volume production runs, while investment casting may be more suitable for lower volume production.
- Part complexity: For intricate parts with fine details, investment casting may be the better option, whereas die casting is better suited for simpler geometries.
- Material requirements: Consider the material properties required for the part, as die casting and investment casting support different ranges of materials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both die casting and investment casting offer unique advantages and limitations that make them ideal for specific applications. Understanding the differences between the two processes and considering factors such as production volume, part complexity, and material requirements will help you determine which process is best suited for your project. Whether you need high volume production with tight tolerances or intricate parts with fine details, choosing the right casting method can make all the difference in the quality and efficiency of your manufacturing process.


















