If you’ve ever marveled at the intricate details of a car’s engine components or the sturdy feel of a decorative fixture, you might have zinc die casting to thank. This process, though often overshadowed by its aluminum counterpart, is a cornerstone in manufacturing. But what exactly is zinc die casting, and why should you care? Let’s dive in and explore this fascinating world.
What is Zinc Die Casting?

Zinc die casting is a manufacturing process where molten zinc is injected into a mold to create precise and complex metal parts. This method is favored for its ability to produce high volumes of identical parts with tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes. It’s like baking a cake, but instead of batter, you have molten metal, and instead of a cake, you get durable, detailed metal components.
The Zinc Die Casting Process
The process of zinc alloy die casting is quite methodical, involving several key steps to ensure the final product meets stringent quality standards.

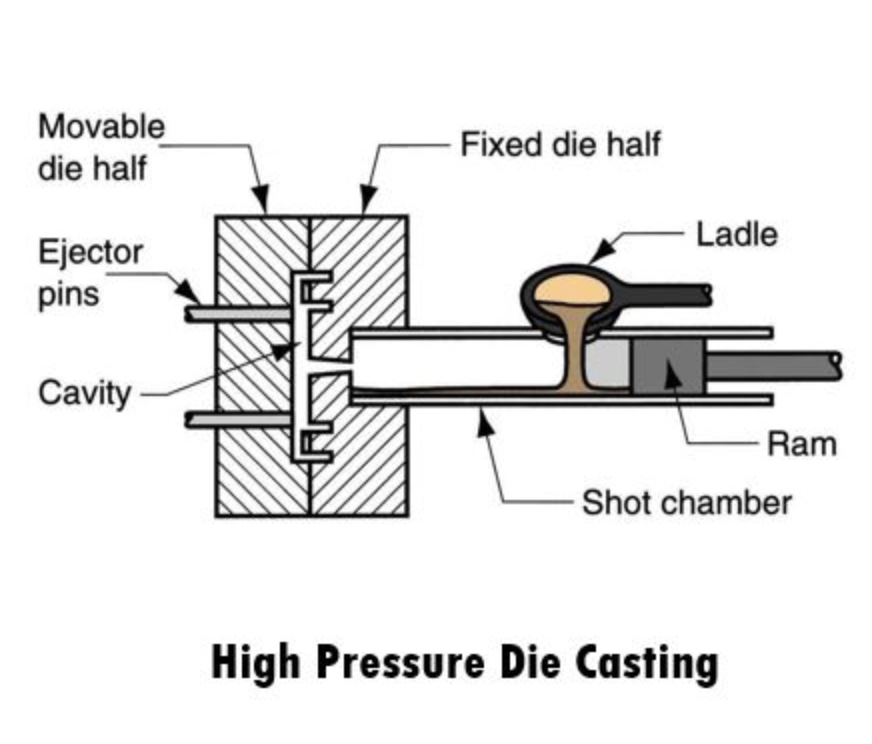
Step #1: Melting and Injection
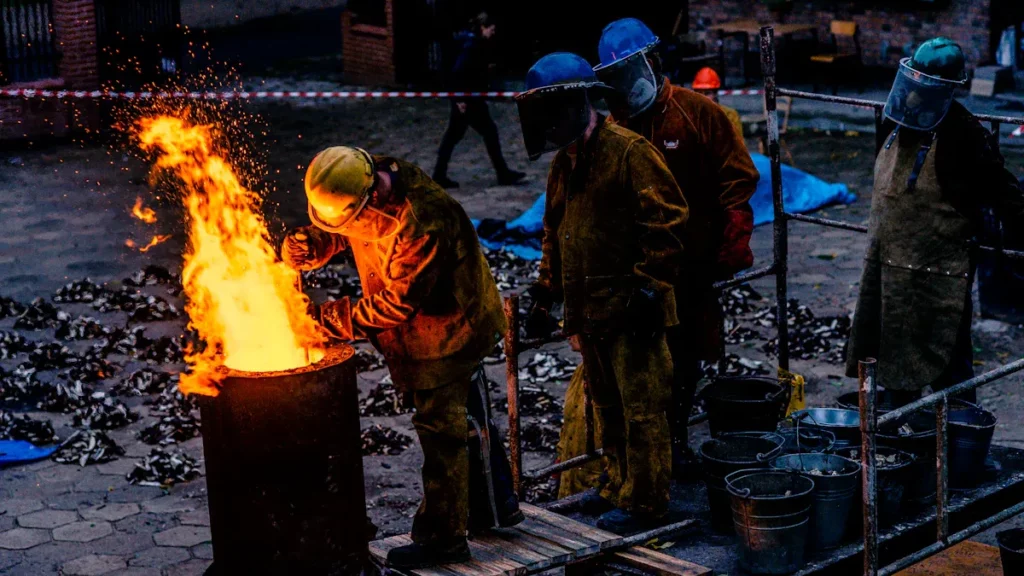
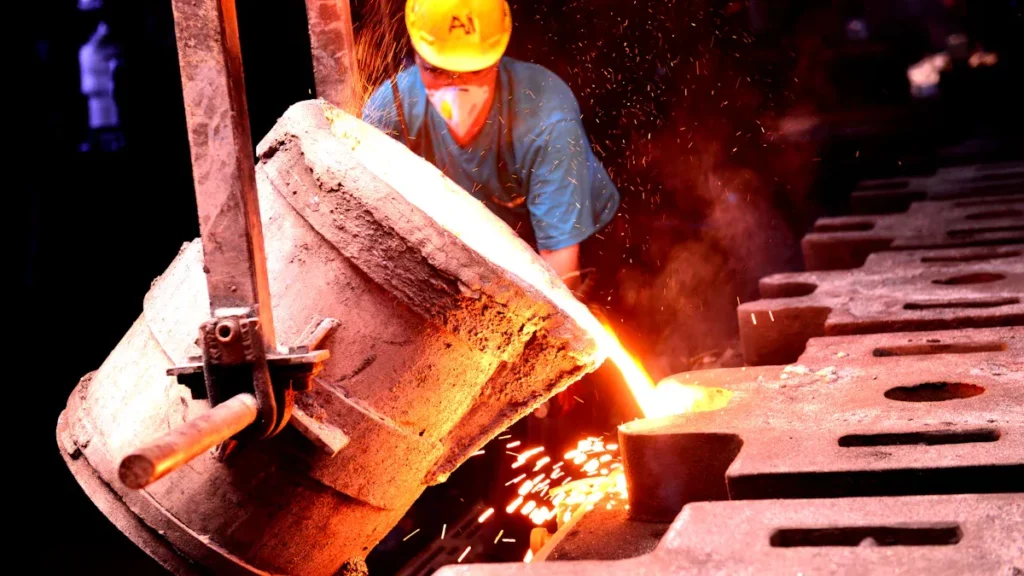
First, zinc alloy ingots are melted in a furnace until they become a liquid at around 800 degrees Fahrenheit. This molten zinc is then injected under high pressure into a steel mold, known as a die. Imagine a giant syringe pushing metal into a mold with precision and speed.
Step #2: Cooling and Solidification
Once the molten zinc fills the mold, it is allowed to cool and solidify. This step is crucial as it determines the final shape and structural integrity of the cast part. Think of it like letting your cake cool before taking it out of the pan to avoid crumbling.
Step #3: Ejection and Trimming
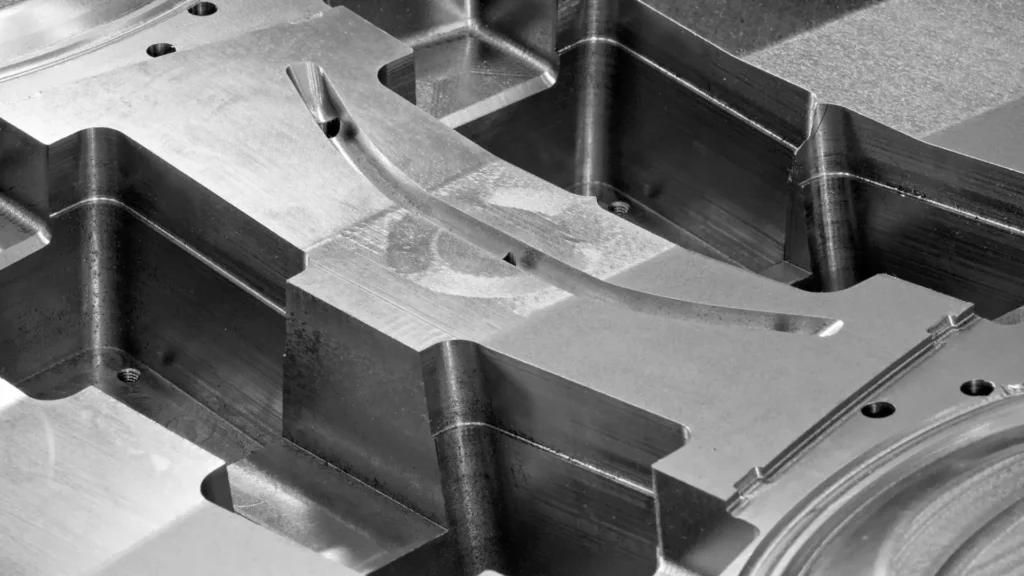
After the part has cooled, it’s ejected from the die. However, it’s not quite ready yet. The next step involves trimming any excess material, known as flash, to ensure the part meets the desired specifications. This is akin to frosting your cake, making sure it looks as good as it tastes.
Popular Zinc Alloys in Die Casting
Zinc die casting isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. Different alloys are used depending on the application, with each offering unique properties.
Zamak Alloys
Zamak alloys are among the most commonly used in zinc die casting, prized for their strength and versatility.
- Zamak 3: Zamak 3 is the workhorse of zinc alloys. It offers a great balance of strength, ductility, and impact resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Zamak 5: For applications requiring higher hardness and strength, Zamak 5 is the go-to choice. It has slightly higher copper content, enhancing its mechanical properties.
- Zamak 2: Zamak 2 is known for its exceptional strength and hardness, though it’s less ductile than other Zamak alloys. It’s ideal for parts that need to endure heavy wear and tear.
ZA Alloys
ZA alloys (Zinc-Aluminum) are another category, offering a different set of characteristics.
- ZA-8: ZA-8 is renowned for its excellent casting characteristics and strength, making it ideal for smaller, more intricate parts.
- ZA-12: With a higher aluminum content, ZA-12 offers superior hardness and wear resistance, suitable for components exposed to friction.
- ZA-27: ZA-27 boasts the highest strength and lowest density of all zinc alloys, making it perfect for parts that need to be both strong and lightweight.
Advantages of Zinc Die Casting
Why choose zinc die casting over other methods? Here are some compelling reasons:
High Production Efficiency
The die casting process, especially zinc die casting, allows for high-speed and large-volume production. Hot chamber die casting machines can achieve an average of 400 to 900 castings per hour, significantly increasing production efficiency.
High Dimensional Accuracy
Die castings exhibit high dimensional accuracy, typically achieving tolerances of IT13 to IT15 according to GB 1800-2009, and in some cases, even up to IT10 to IT11. This allows die castings to meet the demands of precision components.
Excellent Surface Quality
Die castings possess a high surface quality, with surface roughness values ranging from Ra 3.2 to 1.6 μm, and locally achieving Ra 0.8 μm. This high-quality surface reduces the need for subsequent processing, lowering costs.
Ability to Cast Complex Thin-Walled Parts
Zinc die castings can have complex part shapes while maintaining thin wall thicknesses, with the minimum wall thickness of zinc alloy die castings reaching 0.3 mm.
Good Mechanical Properties
Metal melts cool rapidly in the die casting mold under pressure, resulting in a fine-grained and dense structure near the surface. This gives die castings higher strength and hardness.
Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting
No process is perfect. Zinc die casting has its drawbacks:
High Equipment Costs
The cost of casting equipment and molds is high, increasing the initial investment cost. Therefore, die casting is generally suitable for mass production of large quantities of products.
Susceptibility to Gas Porosity
Due to the very high speed at which metal melts fill the mold cavity during die casting, and the non-permeability of mold materials, die castings produced using traditional die casting methods are prone to gas porosity. This can affect the strength and performance of die castings.
High Mold Requirements
Mold design and manufacturing require high precision and quality to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of die castings. This increases the cost and difficulty of mold manufacturing.
High Raw Material Requirements
Die casting has high requirements for the purity and alloy composition of raw materials. Unsuitable raw materials may lead to defects or performance degradation in die castings.
Complex Post-Processing
While die castings have a good surface quality, they may still require subsequent processing such as grinding, polishing, or coating in certain applications to further enhance their performance or appearance.
Applications of Zinc Die Cast Parts
Zinc die casting is used in various industries, thanks to its versatility and strength.
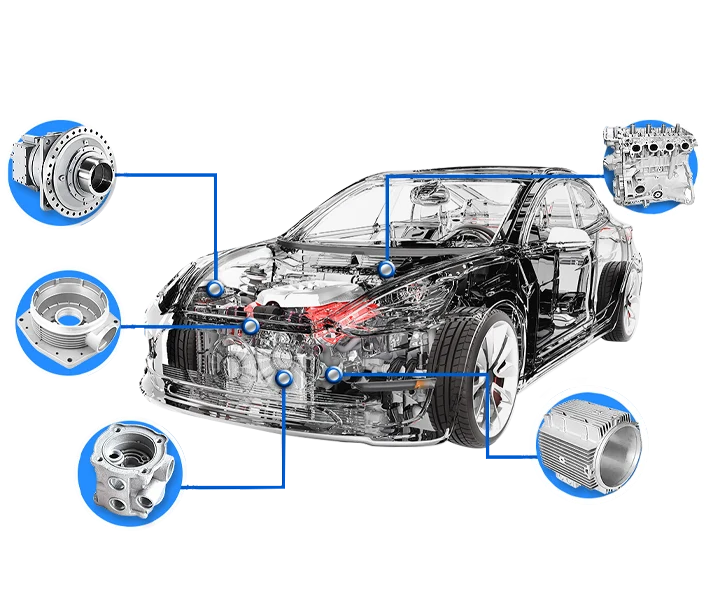
Automotive Industry
Zinc die cast parts are essential in the automotive industry.
- Engine Components: Parts like fuel pumps and carburetors benefit from zinc die casting’s precision and durability.
- Interior and Exterior Parts: From door handles to intricate trim, zinc die cast parts add both function and flair to vehicles.
Electronics and Electrical Components
Zinc die casting ensures durability and reliability for the electronic parts.
- Housing for Electronic Devices: Strong, durable casings for devices protect delicate internal components.
- Connectors and Terminals: Zinc’s conductivity and strength make it ideal for electrical connectors and terminals.
Consumer Goods
In our everyday lives, zinc die casting shows up in countless items.
- Handles and Hardware: Think of the solid feel of a drawer handle or the robustness of a door lock—thank zinc die casting for that.
- Decorative Fixtures: From stylish lamp bases to ornate picture frames, zinc die cast parts are both beautiful and functional.
Zinc vs. Aluminum Die Casting
When it comes to die casting, zinc and aluminum die casting each have their strengths.

Strengths and Weaknesses
Is zinc stronger than aluminum? Yes, zinc is stronger and more durable, but heavier. Aluminum is lighter and offers better corrosion resistance but isn’t as strong.
Ideal Applications for Each
Zinc alloys are suitable for parts that need strength and durability. Aluminum suits for components where weight savings and corrosion resistance are paramount.
Conclusion
Zinc die casting is a fascinating and vital manufacturing process, offering unmatched precision, strength, and versatility. From automotive components to consumer goods, its applications are vast and varied. While it has its drawbacks, the benefits often outweigh the negatives, making zinc die casting a go-to choice for many industries. When looking for high-quality zinc die casting components, you can collaborate with zinc alloy die casting parts manufacturers who offer precision, durability, and cost-effective solutions for various industrial applications.
FAQs
1. What is the main advantage of zinc die casting over other methods?
Zinc die casting offers superior precision and the ability to create complex geometries, making it ideal for detailed and high-volume production.
2. Are zinc die cast parts recyclable?
Yes, zinc die cast parts are fully recyclable, making this process environmentally friendly.
3. How does zinc die casting compare to plastic injection molding?
While plastic injection molding is lighter and cheaper for some applications, zinc die casting provides greater strength, durability, and thermal stability.
4. Can zinc die cast parts be painted or plated?
Absolutely! Zinc die cast parts can be easily painted or plated for enhanced aesthetics and additional corrosion resistance.
5. What industries benefit the most from zinc die casting?
The automotive, electronics, and consumer goods industries are some of the biggest beneficiaries of zinc die casting, thanks to its precision, strength, and cost-effectiveness.
6. What metal is most frequently used in the casting process?
Aluminum is the most frequently used metal in the casting process, favored for its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and versatility across various industries.