Casting -Prozesse sind seit Jahrhunderten von entscheidender Bedeutung in der verarbeitenden Industrie, Ermöglichen der Erstellung komplexer und komplizierter Metallkomponenten. Vom Sandguss bis zum Präzisionsguss, Es gibt verschiedene Methoden zur Herstellung von hochwertigen Gussteilen für eine Vielzahl von Branchen. In diesem Artikel, Wir werden erforschen 11 Verschiedene Arten von Gussprozessen, Bereitstellung von Einsichten in die Vor- und Nachteile jeder Methode.
Tabelle im Vergleich der 11 Arten von Gießprozessen
| Casting-Prozess | Produktionsvolumen | Materialeignung | Kosten |
| Sandguss | Niedrig bis hoch | Vielseitig | Niedrig |
| Druckguss | Hoch | Aluminium, Zink | Hoch |
| Feinguss | Niedrig bis mittel | Stahl, Aluminium | Hoch |
| Schwerkraft stirbt Guss | Mittel bis hoch | Aluminium, Kupfer | Mäßig |
| Vakuumguss | Niedrig bis mittel | Komplizierte Teile | Hoch |
| Kontinuierliches Gießen | Hoch | Stahl, Aluminium | Hoch |
| Schalenform | Mittel bis hoch | Aluminium, Kupfer | Mäßig |
| Casting verloren | Niedrig bis mittel | Aluminium, Eisen | Mäßig |
| Schleuderguss | Niedrig bis mittel | Zylindrische Teile | Mäßig |
| Dauerhaftes Schimmelpilzguss | Mittel bis hoch | Aluminium, Magnesium | Hoch |
| Squeeze -Sterbchen | Hoch | Dünnwandige Teile | Mäßig |
Sandguss
Was ist Sandguss?
Sandguss ist einer der ältesten und am weitesten verbreiteten Gussprozesse der Branche. Es beinhaltet die Erstellung einer Form aus Sand, in welches geschmolzene Metall gegossen wird, um die gewünschte Form zu erzeugen. Sobald das Metall verfestigt ist, Die Sandform ist auseinander unterbrochen, um den letzten Teil zu enthüllen.
Vor- und Nachteile von Sandguss
Einer der Hauptvorteile des Sandgusses ist seine Vielseitigkeit, Ermöglichen der Produktion von großer, Komplexe Teile mit relativ geringen Werkzeugkosten. Jedoch, Sandguss kann zeitaufwändig sein und zu einer geringeren Genauigkeit im Vergleich zu anderen Gussmethoden führen.
Druckguss
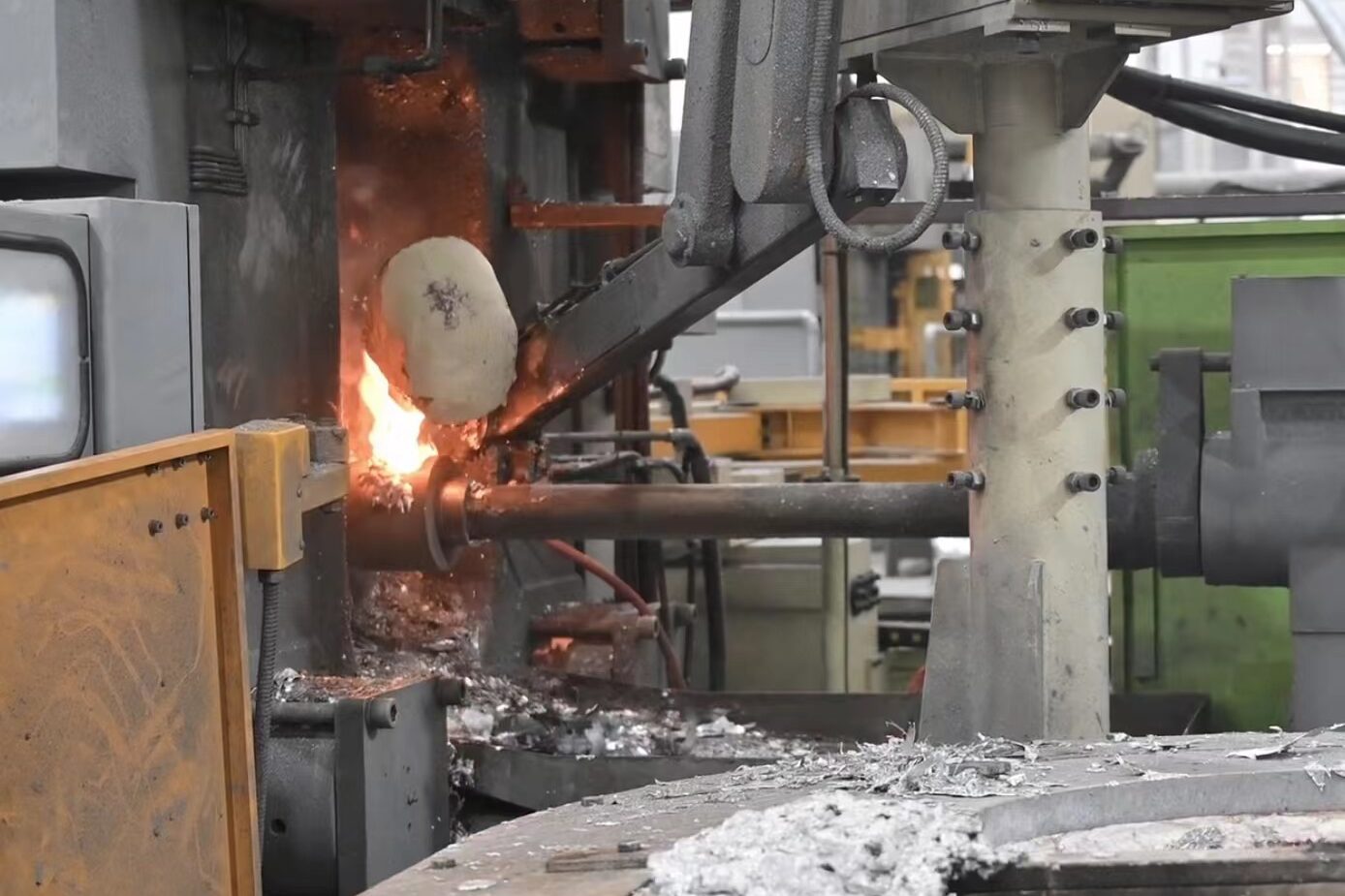

Was ist Druckguss??
Druckguss ist ein Metallgussprozess, bei dem geschmolzenes Metall in eine Stahlform injiziert wird, Bekannt als Würfel. Diese Art des Metallguss, wie zum Beispiel Automatische Teile, Beleuchtungsteile Und elektronische Teile.
Vor- und Nachteile des Castings
Das Casting bietet hohe Produktionsraten und enge Toleranzen, Damit ist es ideal für die Massenproduktion. Jedoch, Die anfänglichen Werkzeugkosten können erheblich sein, und das Casting ist möglicherweise nicht für alle Arten von Legierungen geeignet. Um mehr zu erfahren, siehe unsere Ratgeber zum Thema Druckguss.
Feinguss
Was ist Feinguss??
Feinguss, auch Wachsausschmelzguss genannt, ist ein Prozess, bei dem ein Wachsmuster erstellt wird, mit Keramik beschichten, und dann das Wachs schmelzen, um eine Form zu erzeugen. Molzenes Metall wird dann in die Keramikform gegossen, um den letzten Teil zu erzeugen.
Vor- und Nachteile des Investitionsgastes
Das Investitionsguss ermöglicht die Produktion komplizierter Teile mit hoher Genauigkeit und glattem Oberflächenfinish. Jedoch, Es kann teuer und zeitaufwändig sein, Dadurch besser für kleine bis mittelgroße Produktionsläufe geeignet ist.
Schwerkraft stirbt Guss
Was ist Schwerkraft-Druckguss??
GRAVITY-GRAUS ist ein bewährtes Gießen des Metallprozesses, das eine dauerhafte Form aus Metall verwendet. Diese Metallgussmethode wird häufig zur großen Herstellung verwendet, Symmetrische Teile mit hoher struktureller Integrität.
Vor- und Nachteile von Schwerkraft sterben Casting
GRAVITY DIE GESCHAFT bietet eine hervorragende dimensionale Genauigkeit und mechanische Eigenschaften, Damit es für hochfeste Anwendungen geeignet ist. Jedoch, Die anfänglichen Werkzeugkosten können hoch sein, und der Prozess ist möglicherweise nicht so kostengünstig für kleine Produktionsläufe.
Vakuumguss
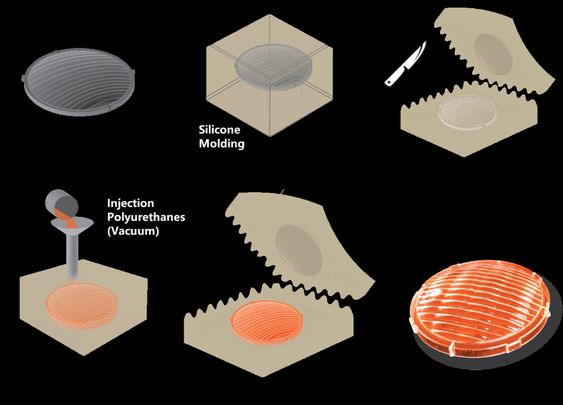
Was ist Vakuumguss?
Vakuumguss ist eine Variation des Investitionsgusses, bei der ein Vakuum zum Zeichnen von geschmolzenem Metall in die Formhöhle verwendet. Diese Methode wird häufig zum Erstellen von Teilen mit komplizierten Details und dünnen Wänden verwendet.
Vor- und Nachteile von Vakuumguss
Das Vakuumguss bietet hohe Präzision und Oberflächenbeschaffung, Es ist ideal, um komplexe Teile mit engen Toleranzen zu erzeugen. Jedoch, Der Prozess kann teuer sein, und das Risiko einer Porosität im letzten Teil kann im Vergleich zu anderen Gussmethoden höher sein.
Kontinuierliches Gießen
Was ist kontinuierliches Casting?
Continuous Casting ist eine Methode, die zur Erzeugung lang verwendet wird, kontinuierliche Metalllängen durch Gießen geschmolzener Metall in eine wassergekühlte Form. Dieses Verfahren wird üblicherweise zur Herstellung von Stahl- und Aluminium -Börsen verwendet, Platten, und Stangen.
Vor- und Nachteile des kontinuierlichen Gießens
Continuous Casting bietet hohe Produktionsraten und verbesserte mechanische Eigenschaften im Endprodukt. Jedoch, Der Prozess erfordert spezielle Geräte und ist möglicherweise nicht für alle Arten von Metallen und Legierungen geeignet.
Schalenform
Was ist Schalenform?
Schalenform, Auch als Shell Casting bekannt, ist ein Prozess, bei dem eine mit Harz beschichtete Sandhülle verwendet wird, um den Formhohlraum zu erzeugen. Molzenes Metall wird dann in die Form gegossen, um den endgültigen Teil zu erzeugen, Mit der Schale, die eine hervorragende Oberflächenfinish und die dimensionale Genauigkeit bietet.
Vor- und Nachteile von Schalenform
Das Schalenformwerk bietet hohe Produktionsraten und kann Teile mit komplexen Geometrien produzieren. Jedoch, Der Prozess erfordert möglicherweise zusätzliche Schritte im Vergleich zu anderen Gussmethoden, und die Werkzeugkosten können höher sein.
Casting verloren
Was ist verlorenes Casting verloren?
Gusslost-Foam-Guss ist ein Prozess, bei dem ein Schaummuster verwendet wird, das mit feuerfestem Material beschichtet ist, um die Form zu erstellen. Wenn das geschmolzene Metall in die Form gegossen wird, Das Schaummuster verdampft verdampft, den letzten Teil hinterlassen.
Vor- und Nachteile von Lost-Foam Casting
Das Gießen von verlorener Herkunft ermöglicht die Herstellung komplexer Teile mit engen Toleranzen und minimalen Bearbeitungsanforderungen. Jedoch, Der Prozess kann teuer sein und Einschränkungen hinsichtlich der Teilgröße und der Materialkompatibilität haben.
Schleuderguss
Was ist Zentrifugal -Casting??
Zentrifugalguss ist eine Methode zur Herstellung von zylindrischen Teilen durch Gießen von geschmolzenem Metall in eine rotierende Form. Die Zentrifugalkraft hilft, das Metall gleichmäßig zu verteilen, was zu Teilen mit hoher Dichte und hervorragenden mechanischen Eigenschaften führt.
Vor- und Nachteile des Zentrifugalsgusss
Das Zentrifugalguss bietet eine hohe Metallqualität und ist gut geeignet, um hohle Teile mit gleichmäßiger Wandstärke zu produzieren. Jedoch, Der Prozess kann auf bestimmte Teilgeometrien beschränkt sein, und die Werkzeugkosten können im Vergleich zu anderen Gussmethoden höher sein.
Dauerhaftes Schimmelpilzguss
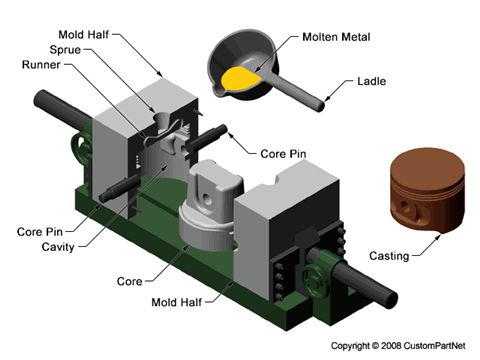
Was ist dauerhaftes Schimmelpilzguss?
Dauerhaftes Schimmelpilzguss, Auch als Gravity -Sterbchen bekannt, beinhaltet die Verwendung einer wiederverwendbaren Metallform zur Herstellung von Teilen. Das geschmolzene Metall wird in die Formhöhle gegossen, wo es festigt, um den letzten Teil zu schaffen.
Vor- und Nachteile von dauerhaftem Schimmelpilzguss
Das permanente Schimmelpack bietet hohe Produktivitätsraten und eine hervorragende Oberflächenbeschaffung, Es ist ideal, um qualitativ hochwertige Teile mit engen Toleranzen zu erzeugen. Jedoch, Die anfänglichen Werkzeugkosten können erheblich sein, und der Prozess ist möglicherweise nicht für alle Arten von Legierungen geeignet.
Squeeze -Sterbchen
Was ist Squeeze -Sterblichkeitsguss?
Squeeze -Würfelguss ist eine Variation des Gussprozesses. Diese Methode wird häufig zum Erstellen von Teilen mit dünnen Wänden und komplizierten Details verwendet.
Vor- und Nachteile des Squeeze -Sterbchens
Squeeze -Würfelguss bietet eine verbesserte Teildichte und verringerte Porosität, was zu Teilen mit höherer Festigkeit und Haltbarkeit führt. Jedoch, Der Prozess kann teurer und komplexer sein als herkömmliche Gussmethoden.
Was ist Casting?
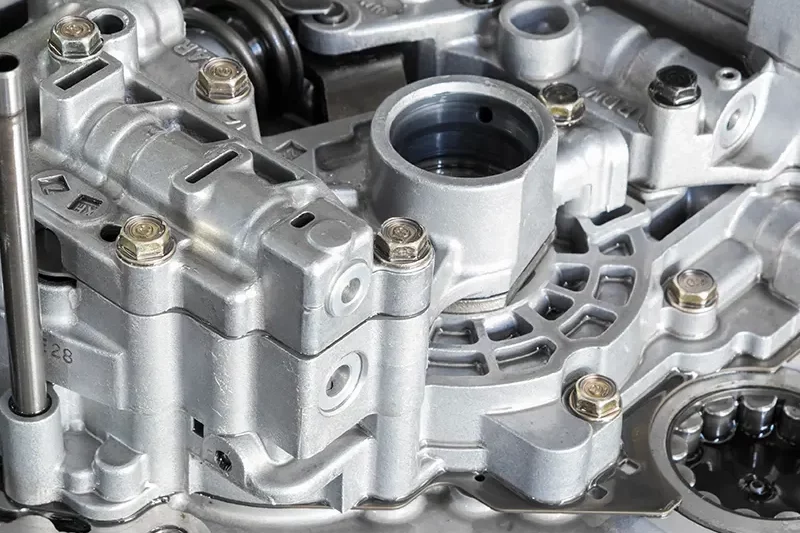
Gießen ist ein Herstellungsprozess, bei dem geschmolzenes Metall in eine Form gegossen wird, um eine bestimmte Form oder Form zu erzeugen. Diese Methode wird in verschiedenen Branchen häufig verwendet, einschließlich Automotive, Luft- und Raumfahrt, und Bau, Teile mit komplexen Geometrien und überlegenen mechanischen Eigenschaften herstellen.
Wie funktioniert das Casting??
Casting funktioniert, indem eine Form erstellt wird, die der gewünschten Form des letzten Teils entspricht. Dann wird geschmolzenes Metall in den Formhöhle gegossen, wo es sich verfolgt, um den fertigen Teil zu bilden. Sobald das Metall abgekühlt und verhärtet ist, der Schimmel wird entfernt, den Gussteil hinterlassen.
Was sind die Materialien, die beim Gießen verwendet werden??
Die beim Gießen verwendeten Materialien können je nach dem spezifischen Prozess und den Anforderungen des produzierten Teils variieren. Gemeinsame Materialien, die beim Gießen verwendet werden Aluminium, Stahl, Eisen, Messing, und Kupfer, unter anderem. Jedes Material bietet einzigartige Eigenschaften und Vorteile für verschiedene Anwendungen.
So wählen Sie eine Art Casting -Prozess aus?
Bei der Auswahl der richtigen Art des Gussprozesses unter den 11 Verschiedene Arten von Metallgussoptionen, Es sind mehrere Schlüsselfaktoren zu berücksichtigen. Hier sind einige wichtige Punkte, die Sie beachten sollten:
- Teilkomplexität: Betrachten Sie die Komplexität des Teils, den Sie produzieren müssen. Einige Gussprozesse, wie Investitionskaste und Präzisions -Casting, sind besser für komplizierte und detaillierte Teile geeignet, während andere, wie Sandguss, kann für einfachere Formen geeigneter sein.
- Produktionsvolumen: Denken Sie über das Volumen der Teile nach, die Sie produzieren müssen. Für hochvolumige Produktionsläufe, Prozesse wie das Casting und das dauerhafte Schimmelpilzguss sind ideal aufgrund ihrer hohen Produktionsraten und Effizienz.
- Materialbedarf: Betrachten Sie die Art der Metall oder Legierung, die Sie für Ihre Teile verwenden möchten. Bestimmte Gussprozesse können besser für bestimmte Materialien geeignet sein. Zum Beispiel, Zentrifugalguss wird häufig zum Herstellen von zylindrischen Teilen von Metallen wie Stahl und Aluminium verwendet.
- Kostenbeschränkungen: Bewerten Sie die anfänglichen Werkzeugkosten, Produktionskosten, und Gesamtkosten, die mit jedem Casting -Prozess verbunden sind. Einige Methoden erfordern möglicherweise höhere Vorabinvestitionen, Bieten Sie jedoch langfristige Kosteneinsparungen in Bezug auf Produktionseffizienz und Teilqualität an.
- Qualitätskontrolle: Berücksichtigen Sie die für Ihre Teile erforderliche Präzisions- und Qualitätskontrolle. Prozesse wie Präzisionsguss und Schalenform bieten eine hohe dimensionale Genauigkeit und Oberflächenbeschaffung, Sie für kritische Anwendungen geeignet machen, die überlegene Qualitätsstandards erfordern.
Auswahl der richtigen Casting -Hersteller
Die Auswahl des richtigen Casting -Herstellers ist entscheidend, um die Qualität und Konsistenz der endgültigen Teile sicherzustellen. Faktoren bei der Auswahl zu berücksichtigen ein zuverlässiger Casting -Hersteller ihre Erfahrung einbeziehen, Fähigkeiten, Qualitätskontrollprozesse, und Fähigkeit, Produktionsfristen einzuhalten. Es wird empfohlen, eng mit einem seriösen Hersteller zusammenzuarbeiten, der während des gesamten Casting -Prozesses Anleitungen und Unterstützung bieten kann.
Abschluss
Abschließend, Es gibt verschiedene Arten von Gussprozessen zur Herstellung von hochwertigen Metallteilen mit komplexen Geometrien und überlegenen mechanischen Eigenschaften. Vom Sandguss bis zum Präzisionsguss, Jede Methode bietet einzigartige Vor- und Nachteile, die vor der Auswahl des am besten geeigneten Prozesss sorgfältig ausgewertet werden sollten. Durch das Verständnis der unterschiedlichen Gusstechniken und Berücksichtigung von Faktoren wie der Teilkomplexität, Produktionsvolumen, und materielle Anforderungen, Hersteller können den richtigen Gussprozess auswählen, um ihre spezifischen Anforderungen zu erfüllen und optimale Ergebnisse zu erzielen.


















